Next: Incorrect migration velocity
Up: Correct migration velocity
Previous: Discussion
In 2-D, the offset-to-angle transformation is done with the relation
| 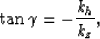 |
(1) |
where 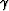 is the aperture angle of the reflection,
kh is the offset wavenumber associated with the
subsurface horizontal offset, and
kz is the vertical wavenumber.
Tisserant and Biondi (2003) presented a 3-D generalization
of Equation 1:
is the aperture angle of the reflection,
kh is the offset wavenumber associated with the
subsurface horizontal offset, and
kz is the vertical wavenumber.
Tisserant and Biondi (2003) presented a 3-D generalization
of Equation 1:
| 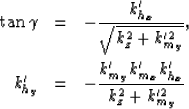 |
(2) |
| (3) |
where 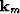 and boldk_h are the midpoint and offset vector
wavenumber, respectively, and where the reflection azimuth,
and boldk_h are the midpoint and offset vector
wavenumber, respectively, and where the reflection azimuth, 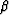 ,
is introduced through
,
is introduced through
| 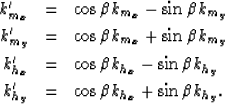 |
(4) |
| (5) |
| (6) |
| (7) |
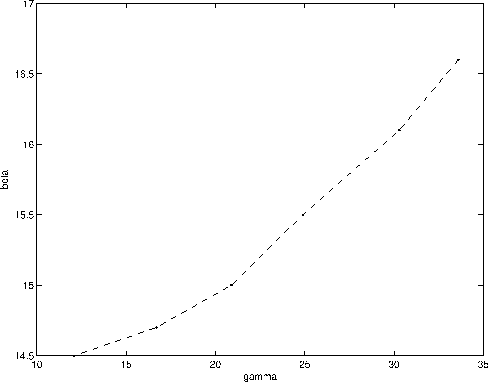
The offset-to-angle transforms a
(kz,kmx,kmy,khx,khy) five dimensions cube into
another 5-D one 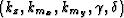 .Figure
.Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) is the measured
aperture-azimuth
distribution for the configuration displayed in Figure
is the measured
aperture-azimuth
distribution for the configuration displayed in Figure
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) obtained with ray-tracing.
We set the lower boundary in
obtained with ray-tracing.
We set the lower boundary in 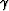 because of an increased
incertitude in the estimation of
because of an increased
incertitude in the estimation of 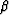 as
as 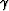 gets close to .
The upper boundary in
gets close to .
The upper boundary in 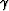 is reached when one of the two rays
begins to overturn.
is reached when one of the two rays
begins to overturn.

We now present a more complex 3-D extension: the one addressing
the 3-D full prestack migration with a wrong migration velocity.





Next: Incorrect migration velocity
Up: Correct migration velocity
Previous: Discussion
Stanford Exploration Project
10/14/2003
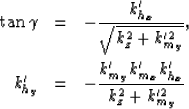
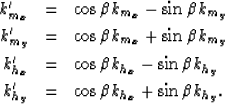
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) is the measured
aperture-azimuth
distribution for the configuration displayed in Figure
is the measured
aperture-azimuth
distribution for the configuration displayed in Figure
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) obtained with ray-tracing.
We set the lower boundary in
obtained with ray-tracing.
We set the lower boundary in ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif)