Next: Patchy-Saturation Modeling Choices
Up: Patchy-Saturation Transport
Previous: High-frequency limit of
The high- and low-frequency limits of 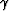 are then connected by a simple frequency
function to obtain the final model
are then connected by a simple frequency
function to obtain the final model
| 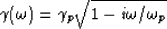 |
(79) |
where the transition frequency 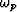 is defined
is defined
| 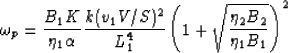 |
(80) |
and where 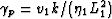 . Equation (79)
has a single singularity (a branch point) at
. Equation (79)
has a single singularity (a branch point) at 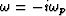 .
Causality requires that with an
.
Causality requires that with an 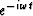 time dependence,
all singularities and zeroes of a transport coefficient like
time dependence,
all singularities and zeroes of a transport coefficient like 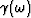 must reside in the lower-half complex
must reside in the lower-half complex 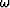 plane.
Equation (79) satisfies this physically important constraint.
plane.
Equation (79) satisfies this physically important constraint.





Next: Patchy-Saturation Modeling Choices
Up: Patchy-Saturation Transport
Previous: High-frequency limit of
Stanford Exploration Project
10/14/2003
![]() are then connected by a simple frequency
function to obtain the final model
are then connected by a simple frequency
function to obtain the final model