Next: Work to be done
Up: Completed steps towards the
Previous: Deep-origin FEAVO effects can
In order to invert, one must extract the anomalies. Since they are
expressed both in the midpoint-angle domain and in the angle-domain
common image gathers, their separation must proceed in a synergistic
fashion. Figure 6 shows they bear a striking
morphological resemblance to channels, so pattern-recognition techniques
applied to a coherence volume Marfurt et al. (1998) of the prestack cube
may yield good results. Another way to discriminate them may be
building a dip volume Fomel (2000) using plane-wave
destructors Claerbout (1991). This may be successful
because it is actually biomimicry: the human eye discriminates the anomalies
based on their dip, or in the case of the data-domain hyperbola sags,
on the discontinuities in the dip (dip derivative). These
morphological approaches may be corroborated with spectral
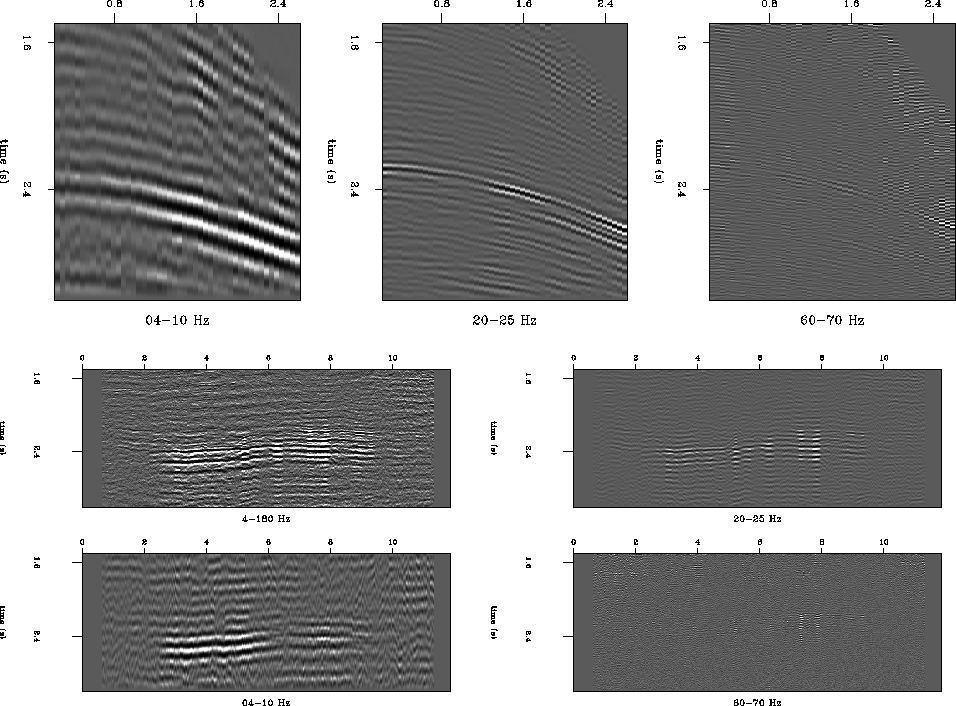
discrimination. In some cases, such as for the Grand Isle dataset, the
FEAVO-causing velocity anomalies are small enough that different
wavelengths may be affected differently (Figure 8).
kfdp
Figure 8 Top: CMP gather at 4.7 km,
filtered with 4-10 Hz, 20-25 Hz, 60-70 Hz. Bottom: section with offset
= 1.291km, filtered with 4-180 Hz, 4-10 Hz, 20-25 Hz, 60-70
Hz. Different frequency bands result in different extents of the FEAVO
anomalies.










Next: Work to be done
Up: Completed steps towards the
Previous: Deep-origin FEAVO effects can
Stanford Exploration Project
6/7/2002