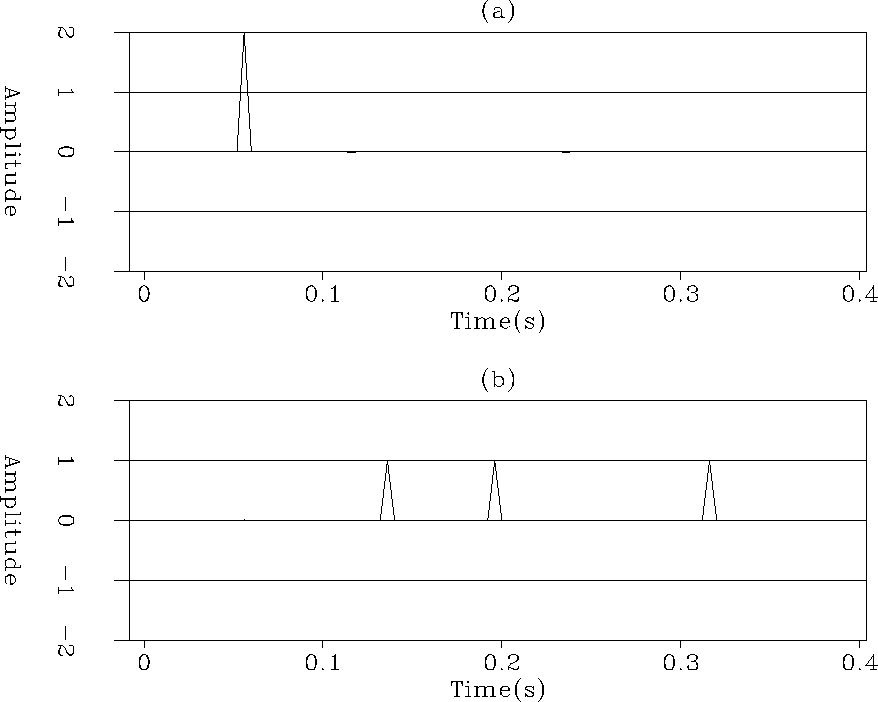Next: Attenuation of internal multiples
Up: A simple 1D problem
Previous: Shaping filters and the
We prove that the 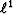 -norm solves the problem highlighted in the
preceding section.
Now our goal is to estimate one shaping filter
-norm solves the problem highlighted in the
preceding section.
Now our goal is to estimate one shaping filter 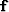 that minimizes
the objective function
that minimizes
the objective function
| 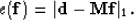 |
(2) |
To achieve this, the shaping filter is estimated iteratively using a nonlinear
conjugate gradient solver (NLCG) as described in Claerbout and Fomel (2001).
The objective function we actually minimize is
| 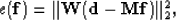 |
(3) |
with
| 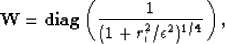 |
(4) |
where ri is the residual for one component of the data space, and  a constant we choose a priori. Equation (3) is minimized with the
standard iteratively re-weighted least-squares approach (Nichols (1994);
Bube and Langan (1997); Guitton (2000))
The objective function in equation (3) amounts to
the
a constant we choose a priori. Equation (3) is minimized with the
standard iteratively re-weighted least-squares approach (Nichols (1994);
Bube and Langan (1997); Guitton (2000))
The objective function in equation (3) amounts to
the 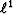 measure when
measure when 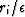 is large and amounts to
the
is large and amounts to
the 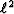 measure when
measure when 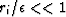 with a smooth transition
between the two.
with a smooth transition
between the two.
In Figure 4, we display the result of the adaptive subtraction
when the 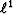 -norm is utilized to estimate the shaping filter
[equation (3) with a small
-norm is utilized to estimate the shaping filter
[equation (3) with a small  ]. The estimated signal
in Figure 4a is perfect, and so is the estimated noise.
It is easy to check that the energy in Figure 4a (e=2) is less
than the energy in Figure 2a (e=3.2) if we use the
]. The estimated signal
in Figure 4a is perfect, and so is the estimated noise.
It is easy to check that the energy in Figure 4a (e=2) is less
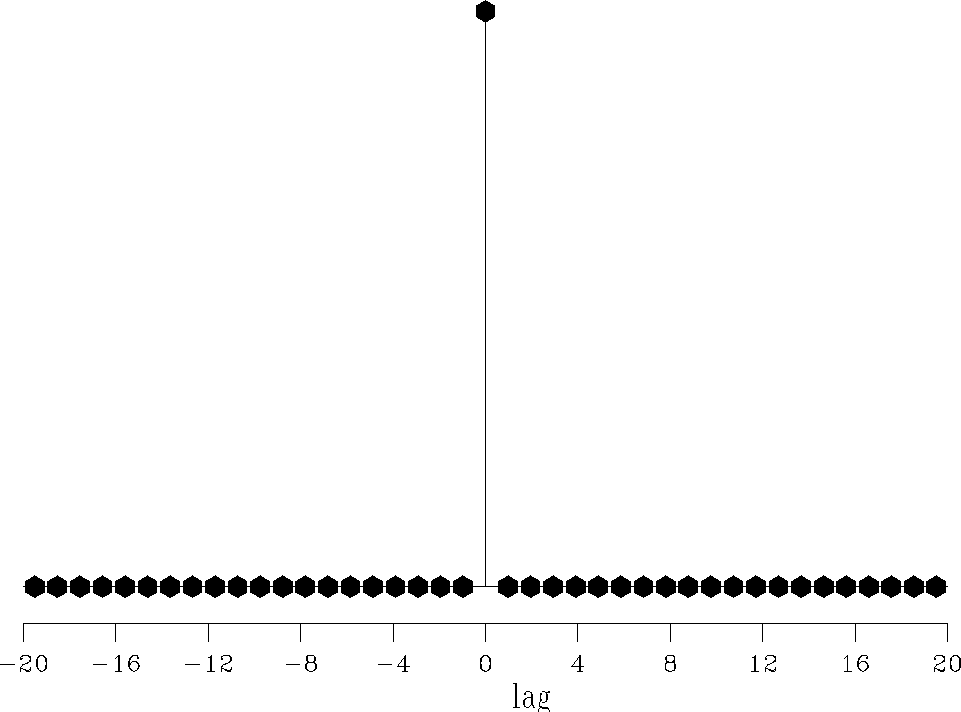
than the energy in Figure 2a (e=3.2) if we use the 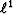 norm. Figure 5 shows the shaping filter associated with the
norm. Figure 5 shows the shaping filter associated with the
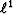 -norm. This filter is a spike at lag=0.
This simple 1D example demonstrates that the
-norm. This filter is a spike at lag=0.
This simple 1D example demonstrates that the 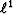 should
be utilized each time significant amplitude differences exist between
multiples and primaries. In the next section, we show another synthetic
example where internal multiples are attenuated.
should
be utilized each time significant amplitude differences exist between
multiples and primaries. In the next section, we show another synthetic
example where internal multiples are attenuated.
1Dl1
Figure 4 (a) The signal estimated with the
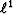 -norm. (b) The noise estimated with the
-norm. (b) The noise estimated with the 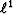 -norm.
-norm.





filterl1
Figure 5 Shaping filter estimated for the
1D problem with the 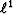 -norm. This filter is a single spike at lag=0. -norm. This filter is a single spike at lag=0.
|
|  |










Next: Attenuation of internal multiples
Up: A simple 1D problem
Previous: Shaping filters and the
Stanford Exploration Project
6/7/2002
![]() -norm is utilized to estimate the shaping filter
[equation (3) with a small
-norm is utilized to estimate the shaping filter
[equation (3) with a small ![]() ]. The estimated signal
in Figure 4a is perfect, and so is the estimated noise.
It is easy to check that the energy in Figure 4a (e=2) is less
than the energy in Figure 2a (e=3.2) if we use the
]. The estimated signal
in Figure 4a is perfect, and so is the estimated noise.
It is easy to check that the energy in Figure 4a (e=2) is less
than the energy in Figure 2a (e=3.2) if we use the ![]() norm. Figure 5 shows the shaping filter associated with the
norm. Figure 5 shows the shaping filter associated with the
![]() -norm. This filter is a spike at lag=0.
This simple 1D example demonstrates that the
-norm. This filter is a spike at lag=0.
This simple 1D example demonstrates that the ![]() should
be utilized each time significant amplitude differences exist between
multiples and primaries. In the next section, we show another synthetic
example where internal multiples are attenuated.
should
be utilized each time significant amplitude differences exist between
multiples and primaries. In the next section, we show another synthetic
example where internal multiples are attenuated.