Next: ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Up: Ecker: AVO Sensitivity
Previous: 2-D MODELING
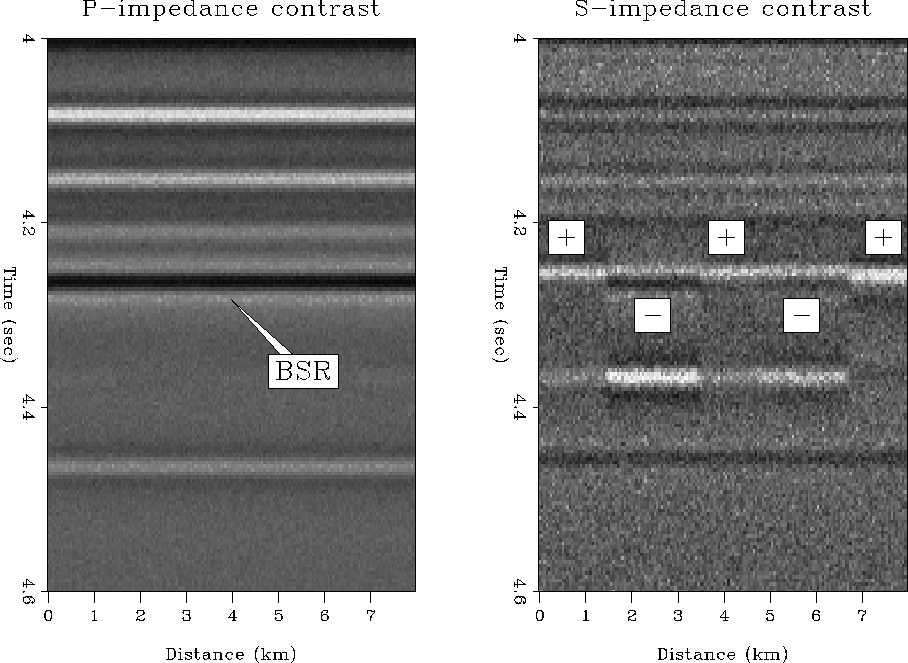
I evaluated the effect of different S-wave velocity contrasts at the BSR
on seismic amplitudes by modeling synthetic CMP gather for different
shear wave velocity contrasts. Increasing velocities display a pronounced
increase of amplitudes with offset. Negative velocity contrasts show either
near to constant AVO behavior or a slight decrease in amplitude with offset. This depends on the magnitude of the contrast itself. AVO analysis of these
single modeled CMP gathers showed that even very small S-wave velocity contrasts of only  17 m/s can be distinguished in the case of ideal amplitudes.
Simulating more realistic data by adding a random Gaussian noise to the data
introduces significant variances in the seismic amplitudes. The resolution
of the different models depends strongly on the data variance, and even a
qualitative analysis to determine the sign of the Vs contrast
(positive or negative) can be impossible. A subsequent 2-D seismic
migration/inversion of a 2-D model suggests that even in the presence of
noise, a reasonably good result can be obtained.
imped-ann
17 m/s can be distinguished in the case of ideal amplitudes.
Simulating more realistic data by adding a random Gaussian noise to the data
introduces significant variances in the seismic amplitudes. The resolution
of the different models depends strongly on the data variance, and even a
qualitative analysis to determine the sign of the Vs contrast
(positive or negative) can be impossible. A subsequent 2-D seismic
migration/inversion of a 2-D model suggests that even in the presence of
noise, a reasonably good result can be obtained.
imped-ann
Figure 9 P-impedance and S-impedance
contrasts for noise-free data.




 imped-noise-ann
imped-noise-ann
Figure 10 P-impedance and S-impedance contrasts for noisy data.




 psmap
psmap
Figure 11 P*S impedance contrast maps for noise-free data (right panel) and noisy data (right panel).










Next: ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Up: Ecker: AVO Sensitivity
Previous: 2-D MODELING
Stanford Exploration Project
11/11/1997