![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/foot_motif.gif) or -1 if there is no trace at that gridding location.
or -1 if there is no trace at that gridding location.
/******************************************************
Keys Object
*******************************************************/
typedef struct KEY {
char name[MAXLABEL]; /* Name of Header Key */
int type; /* Type of Header Key */
int pos; /* Header Key Position in Header Record */
} KEY_o;
/******************************************************
Header Object
*******************************************************/
typedef struct HEADER {
int n_keys; /* Number of Header Keys */
KEY_o *keys; /* Vector of lenght n_keys containig key
objects */
int n_records; /* Number of Header Records */
int record_size; /* Number of bytes in Header Records */
char *values; /* Vector containing Records Values */
} HEADER_o;
The Data Values 2-D Field is a memory representation of the SEPlib90 Data
Values File. The SEPlib90 data types supported are: scalar_byte,
scalar_int, scalar_int, scalar_float, vec3_byte and vec3_float.
The corresponding AVS output types are: scalars char, short, int, float,
and 3-vector char and float.
The third output, Grid Values, provides information about the superimposed,
regular grid.
The
The Grid Values file is a n-D, scalar AVSfield_int,
where each value
represents is equal to the index of
the
corresponding trace and header in the Data Values Field and Header Values
structure![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/foot_motif.gif) or -1 if there is no trace at that gridding location.
or -1 if there is no trace at that gridding location.
|
ReadSep90
Figure 1 Control panel for the Read Sep90 module. | 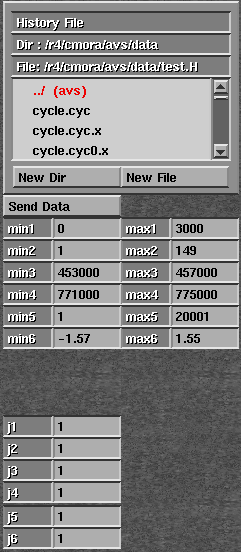 |
A file browser widget is used to select the name of the History file associated with the input data set. The min and max type-in widgets allow the specification of minimum and maximum values for each axis. Axis 1 refers to time axis, and Axis 2 to Axis n refer to the Gridding coordinate system axes. The j widgets allow the user to specify an under-sampling rate along each Gridding coordinate system axis. Once the user has finished with the parameter specification, the Send Data one-shot widget should be selected to read the SEPlib90 data set and pass the output information to downstream modules.