Duri engineers estimate that steam is injected into the reservoir
at the wellbore at about 430 ![]() F and 350 psia.
At the steam front between steam and hot condensate,
the pressure and temperature
may initially be about 250 psia and 350
F and 350 psia.
At the steam front between steam and hot condensate,
the pressure and temperature
may initially be about 250 psia and 350 ![]() F, and later drop to 135 psia
and 350
F, and later drop to 135 psia
and 350 ![]() F as the steamflood matures Bee et al. (1994).
Residual oil saturation in the steam zone is estimated to be about
10% with gas saturation at 90%.
In the hot water and hot oil annulus, temperatures drop off between
the steamfront values and ambient reservoir values of 100
F as the steamflood matures Bee et al. (1994).
Residual oil saturation in the steam zone is estimated to be about
10% with gas saturation at 90%.
In the hot water and hot oil annulus, temperatures drop off between
the steamfront values and ambient reservoir values of 100 ![]() F and 100 psia.
Residual oil saturation may be as high as 20%, and gas saturation
is probably negligible.
In the pressure-front region, pressure values of 110 psia or more
will be above bubble point at an ambient temperature 100
F and 100 psia.
Residual oil saturation may be as high as 20%, and gas saturation
is probably negligible.
In the pressure-front region, pressure values of 110 psia or more
will be above bubble point at an ambient temperature 100 ![]() F.
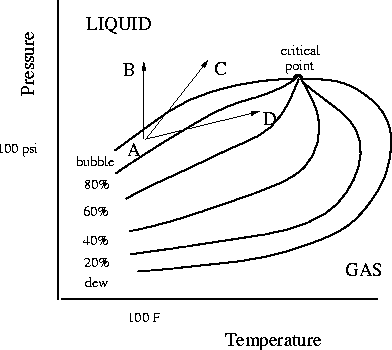
Residual gas saturation is likely to be negligible since
initial gas in pores space crosses the bubble point and dissolves
into liquid oil (path AB of Figure 10).
The pressure, temperature and gas saturation changes expected in the reservoir
during steam injection are tabulated in Table 2 respectively.
F.
Residual gas saturation is likely to be negligible since
initial gas in pores space crosses the bubble point and dissolves
into liquid oil (path AB of Figure 10).
The pressure, temperature and gas saturation changes expected in the reservoir
during steam injection are tabulated in Table 2 respectively.
| ZONE | P (psia) | T (F) | Sg (%) | |||
| steam | 250 | +150 | 350 | +250 | 90 | +80 |
| hot water | 200 | +100 | 250 | +150 | -10 | |
| hot oil | 175 | +75 | 175 | +75 | -10 | |
| pressure front | 150 | +50 | 100 | +0 | -10 | |
| ambient | 100 | -- | 100 | -- | 10 | -- |
 |