Circularly symmetric lowpass filters can be designed by assuming an idealized frequency response of the form
| |
(7) |
![\begin{displaymath}
max [W(f)\left(\sum_{n=0}^{N} {a(n)\cos(nf) - F_0(f)}\right)]\end{displaymath}](img17.gif)
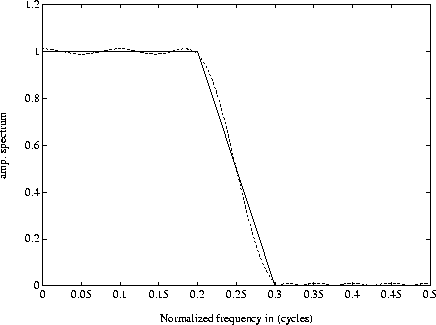
Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) shows the desired and the fitted spectrum
obtained using a 21 term zero-phase filter. The filter in the space domain
is a symmetrical filter as shown in Figure
shows the desired and the fitted spectrum
obtained using a 21 term zero-phase filter. The filter in the space domain
is a symmetrical filter as shown in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) . The filter
coefficients correspond to hn in Figure
. The filter
coefficients correspond to hn in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
The McClellan transformation
filter is designed using the 5x5 filter shown in the Appendix. This
filter corresponds to the G filter shown in Figure
.
The McClellan transformation
filter is designed using the 5x5 filter shown in the Appendix. This
filter corresponds to the G filter shown in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
Once the filter coefficients hn are computed they are incorporated into the
recursive structure shown in Figure
.
Once the filter coefficients hn are computed they are incorporated into the
recursive structure shown in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) . The implementation
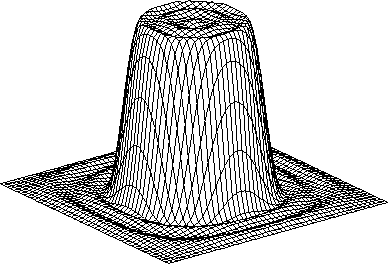
is done in both space and wavenumber domains. The wavenumber domain
response of the filter is shown in Figure
. The implementation
is done in both space and wavenumber domains. The wavenumber domain
response of the filter is shown in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
A spike in x-y space was used to test the space-domain implementation.
The output of
the lowpass filter is a smoothed spike as shown in Figure
.
A spike in x-y space was used to test the space-domain implementation.
The output of
the lowpass filter is a smoothed spike as shown in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif)
 |
|
park
Figure 4 Twenty-one coefficient symmetric 1-D filter in the space domain corresponding to Fig 3. These are the filter coefficients hn used in the Chebyshev filter structure shown in Figure 2. | 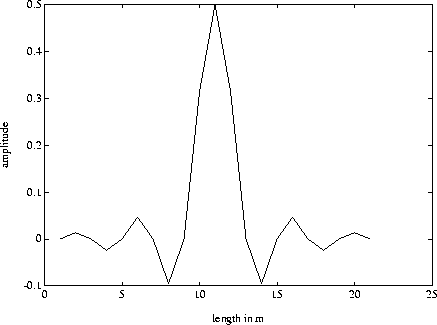 |
 |
|
lowpout
Figure 6 Output of Lowpass Filter in the x-y domain. The filter implementation is in the x-y domain. The modified McClellan filter in space-domain is used to do the transformation. | 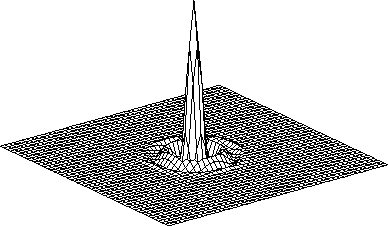 |