




Next: UNDERMIGRATION CAUSED BY PARABOLIC
Up: Mo: Numerical analysis
Previous: Mo: Numerical analysis
Analyses of finite-difference migration errors of the approximations
to the semi-circular dispersion relation by various one-way wave equations
have been given by Claerbout (1976, 1985). However, the effects caused by
sampling in time, space, and depth and the interaction between them have
been largely ignored. Lynn (1976) performed an analysis of group velocity
errors in 15- and 45-degree migration that included the effect of trace
spacing but not that of depth step. Beaumont et al. (1987) presented a
quantitative analysis of the phase errors of finite-difference migration.
A systematic numerical analysis, however, is absent in the literature.
This paper presents a numerical analysis of the constant velocity 15-degree
space-frequency (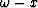 ) time migration algorithm
as a useful step toward a systematic numerical analysis of
finite-difference migration algorithms.
The numerical analysis procedures, I presented, can be extended to
other finite-difference migration algorithms that are implemented in
space-frequency (
) time migration algorithm
as a useful step toward a systematic numerical analysis of
finite-difference migration algorithms.
The numerical analysis procedures, I presented, can be extended to
other finite-difference migration algorithms that are implemented in
space-frequency (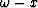 ) and space-time (t-x) domain.
I agree with Nichols (1992) that by optimizing the numerical parameters
used in
) and space-time (t-x) domain.
I agree with Nichols (1992) that by optimizing the numerical parameters
used in 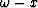 downward continuation, we can use the 15-degree scheme
to migrate higher angles accurately.
The following derivations largely follow Claerbout (1985) in geophysics,
and Moin (1992) in numerical analysis.
downward continuation, we can use the 15-degree scheme
to migrate higher angles accurately.
The following derivations largely follow Claerbout (1985) in geophysics,
and Moin (1992) in numerical analysis.
This paper first explains how the parabolic
approximation of the exact one-way wave equation causes undermigration.
It then shows how the numerical method based on the eigenvalue structure
of the diffraction partial differential equation and the Crank-Nicolson method
causes overmigration.
Finally, it derives the modified wave equation that the numerical
solution actually satisfies for the diffraction equation.





Next: UNDERMIGRATION CAUSED BY PARABOLIC
Up: Mo: Numerical analysis
Previous: Mo: Numerical analysis
Stanford Exploration Project
11/17/1997