The synthetic data are generated with the anti-aliasing
turned on to simulate field arrays. The image is
generated by running kfastaax() with anti=1 and then performing
a causal half-order time derivative.
The effect of simulating field arrays is that
the input impulses are broadened.
The point diffractors appear as
hyperbolic trajectories with a ![]() phase shift on the wavelet.
phase shift on the wavelet.
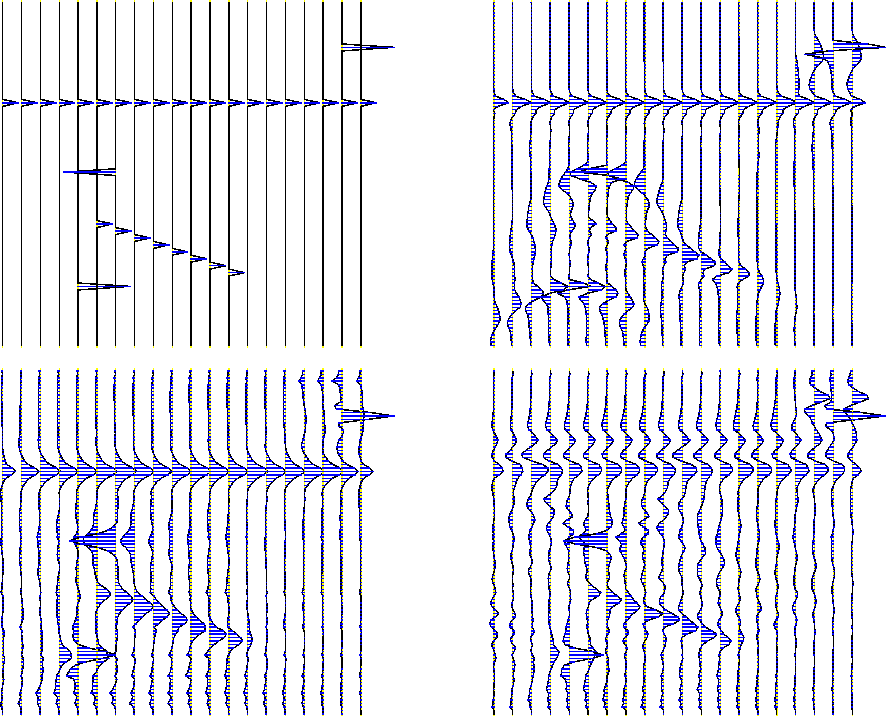
The migrations are performed with (anti=1) and without (anti=0) anti-aliasing and are followed by an anticausal half-order time derivative. The aliased migration (lower right of Figure 1) exhibits systematic noise. The point diffractors have upturned artifacts which appear on adjacent traces as part of a smile-like feature. The flat event has a prominent precursor which looks like a layer above the actual event. Anti-aliasing removes the systematic noise and results in a much better image.
 |