|
layers
Figure 1 Schoenberg-Muir averaging for canted layers. S&M averaging assumes stationarity in the direction of the arrow, and infinite layers in the perpendicular direction. The truncated layers in the shaded block violate these assumptions. | 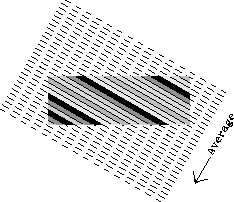 |
In practice, it is known that if the waves propagating through the stack have sufficiently long wavelengths the zero-frequency approximation can be very accurate. The problem of what ``sufficiently long wavelength'' means in practice has been investigated by Nichols (1988). He concluded that if the medium were approximately uniform in the distribution of types of layers on the scale of a wavelength, the wave would not ``feel'' the layers. What about the ``flat infinite layer'' assumption? This assumption is commonly broken when the S&M method is used to model truncated dipping layers (such as those in Figure 1), cracks cross-cutting layers, or non-parallel sets of cracks.
The purpose of this paper is to test how well the method works when applied to truncated dipping layers. For our models we use an annulus of layered media embedded in its S&M homogeneous equivalent. The source is in the center of the annulus. We compare the wavefields after propagation through the annulus with the wavefields in the corresponding homogeneous model.
|
layers
Figure 1 Schoenberg-Muir averaging for canted layers. S&M averaging assumes stationarity in the direction of the arrow, and infinite layers in the perpendicular direction. The truncated layers in the shaded block violate these assumptions. |  |