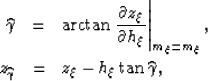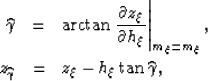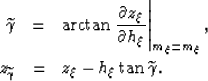Next: RMO analysis in ADCIGs
Up: Residual moveout in anisotropic
Previous: Generalized migration
In 2-D, ADCIGs are computed for each midpoint by applying a
slant-stack decomposition to the prestack image along the
subsurface-offset axis. The kinematics of the angle-domain
transformation are defined by the following change of variable:
| 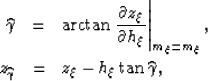 |
(1) |
| (2) |
where 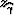 is the transformed image-point depth.
Assuming flat reflectors and VTI media,
Biondi (2005a) demonstrates that the angle
is the transformed image-point depth.
Assuming flat reflectors and VTI media,
Biondi (2005a) demonstrates that the angle
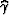 is equal to the phase aperture angle
is equal to the phase aperture angle
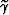 , thereby simplifying
equations 1 and
2:
, thereby simplifying
equations 1 and
2:
| 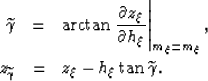 |
(3) |
| (4) |





Next: RMO analysis in ADCIGs
Up: Residual moveout in anisotropic
Previous: Generalized migration
Stanford Exploration Project
5/6/2007