|
flow
Figure 2 Diagram flow for the subsurface-offset transformation to the angle domain. The flow diagram also presents the computation of the individual P-ADCIGs and S-ADCIGs. | 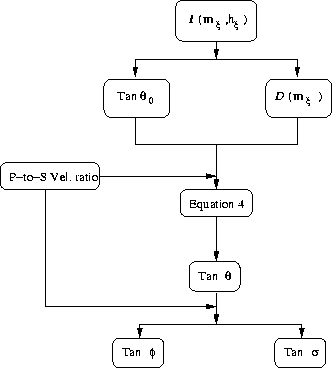 |
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) presents the basic
steps to implement and obtain the angle-domain common-image
gathers for converted-wave data. The first step takes
the final image
presents the basic
steps to implement and obtain the angle-domain common-image
gathers for converted-wave data. The first step takes
the final image |
flow
Figure 2 Diagram flow for the subsurface-offset transformation to the angle domain. The flow diagram also presents the computation of the individual P-ADCIGs and S-ADCIGs. |  |
The following sections present simple synthetic examples as well as a real-data result from the Gulf of Mexico.