




Next: (B) Iterative linearized migration/inversion
Up: (A) Non-iterative linearized migration/inversion
Previous: (2) Wave theory tomography
The conventional prestack migration can be characterized as
| 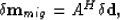 |
(45) |
where AH is a conjugate transpose matrix, which is a back-propagator of the wavefield.
The least-squares prestack migration/inversion imaging can be carried out by the following equation:
| 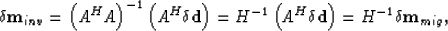 |
(46) |
where H= AHA is a Hessian matrix. The meaning of the Hessian will be discussed in detail. Equation (46) says that the deconvolution of the conventional prestack migration by the inverse of the Hessian produces the migration/inversion results.





Next: (B) Iterative linearized migration/inversion
Up: (A) Non-iterative linearized migration/inversion
Previous: (2) Wave theory tomography
Stanford Exploration Project
11/1/2005