




Next: Adaptive subtraction of multiples
Up: Multidimensional seismic noise attenuation
Previous: Multidimensional seismic noise attenuation
Chapter ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) introduces the Huber norm
Huber (1973). The Huber norm is an hybrid
introduces the Huber norm
Huber (1973). The Huber norm is an hybrid 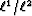 error
measure that is robust to outliers. Because it is differentiable everywhere,
the Huber norm can be minimized with a gradient-based algorithm.
In Chapter
error
measure that is robust to outliers. Because it is differentiable everywhere,
the Huber norm can be minimized with a gradient-based algorithm.
In Chapter ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) , I propose minimizing the Huber norm
with a quasi-Newton method called L-BFGS. This technique can solve any non-linear
problem where local-minima are sought. Its limited-memory requirements make it
also very attractive for solving large-scale problems.
On a velocity estimation problem, this Chapter illustrates
that the Huber norm with the L-BFGS solver is robust to outliers, thus
providing an alternative to the
, I propose minimizing the Huber norm
with a quasi-Newton method called L-BFGS. This technique can solve any non-linear
problem where local-minima are sought. Its limited-memory requirements make it
also very attractive for solving large-scale problems.
On a velocity estimation problem, this Chapter illustrates
that the Huber norm with the L-BFGS solver is robust to outliers, thus
providing an alternative to the 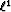 norm.
norm.





Next: Adaptive subtraction of multiples
Up: Multidimensional seismic noise attenuation
Previous: Multidimensional seismic noise attenuation
Stanford Exploration Project
5/5/2005
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) introduces the Huber norm
Huber (1973). The Huber norm is an hybrid
introduces the Huber norm
Huber (1973). The Huber norm is an hybrid ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) , I propose minimizing the Huber norm
with a quasi-Newton method called L-BFGS. This technique can solve any non-linear
problem where local-minima are sought. Its limited-memory requirements make it
also very attractive for solving large-scale problems.
On a velocity estimation problem, this Chapter illustrates
that the Huber norm with the L-BFGS solver is robust to outliers, thus
providing an alternative to the
, I propose minimizing the Huber norm
with a quasi-Newton method called L-BFGS. This technique can solve any non-linear
problem where local-minima are sought. Its limited-memory requirements make it
also very attractive for solving large-scale problems.
On a velocity estimation problem, this Chapter illustrates
that the Huber norm with the L-BFGS solver is robust to outliers, thus
providing an alternative to the