




Next: Noise attenuation by filtering
Up: Multidimensional seismic noise attenuation
Previous: The Huber norm
Chapter ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) illustrates on a multiple
attenuation problem how the Huber norm can help to better
separate primaries from multiples. Adaptive subtraction of multiples
is a two steps process where multiples are first predicted, leading
to an accurate model of the noise, and then adaptively subtracted from the data
by estimating matching filters. When weak multiples are present in the
surroundings of strong primaries, multiples can be matched to
primaries when the
illustrates on a multiple
attenuation problem how the Huber norm can help to better
separate primaries from multiples. Adaptive subtraction of multiples
is a two steps process where multiples are first predicted, leading
to an accurate model of the noise, and then adaptively subtracted from the data
by estimating matching filters. When weak multiples are present in the
surroundings of strong primaries, multiples can be matched to
primaries when the 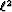 norm is utilized for the filter
estimation step. In this Chapter, I prove that the Huber norm provides
a robust measure for computing filter coefficients that is less
sensitive to the relative strengths of both multiples and primaries,
thus preserving the signal better than the
norm is utilized for the filter
estimation step. In this Chapter, I prove that the Huber norm provides
a robust measure for computing filter coefficients that is less
sensitive to the relative strengths of both multiples and primaries,
thus preserving the signal better than the 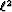 norm.
norm.





Next: Noise attenuation by filtering
Up: Multidimensional seismic noise attenuation
Previous: The Huber norm
Stanford Exploration Project
5/5/2005
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) illustrates on a multiple
attenuation problem how the Huber norm can help to better
separate primaries from multiples. Adaptive subtraction of multiples
is a two steps process where multiples are first predicted, leading
to an accurate model of the noise, and then adaptively subtracted from the data
by estimating matching filters. When weak multiples are present in the
surroundings of strong primaries, multiples can be matched to
primaries when the
illustrates on a multiple
attenuation problem how the Huber norm can help to better
separate primaries from multiples. Adaptive subtraction of multiples
is a two steps process where multiples are first predicted, leading
to an accurate model of the noise, and then adaptively subtracted from the data
by estimating matching filters. When weak multiples are present in the
surroundings of strong primaries, multiples can be matched to
primaries when the