




Next: Experiments
Up: Artman and Sacchi: Inversion
Previous: Development
The condition of using an overcomplete dictionary will hopefully be
satisfied by choosing the number of model space variables to be
roughly two times the number of data points.
While Chen et al. (1999) uses a minimum of four times
oversampling for impressive super resolution results with the Fourier
transform, their examples are normally of the order n=1*103.
Larger dictionaries result in too slow processing for testing purposes.
Due to the fact that the LP infrastructure
imposes a positivity constraint on the solution, we are forced to
solve for a model space twice as large as we would choose with both
negativity and positivity constraints, and then combine the two. We
will use the hyperbolic radon transform (HRT) as the analysis
operator, 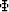 in equation (2) or A in equation
(3). This operator is normally approximately
in equation (2) or A in equation
(3). This operator is normally approximately 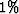 full and,
therefore, a tractable operator to use for this method. As
such, the programming is implemented with a sparse matrix approach rather
than operators as it is traditional at SEP.
full and,
therefore, a tractable operator to use for this method. As
such, the programming is implemented with a sparse matrix approach rather
than operators as it is traditional at SEP.





Next: Experiments
Up: Artman and Sacchi: Inversion
Previous: Development
Stanford Exploration Project
10/14/2003
![]() in equation (2) or A in equation
(3). This operator is normally approximately
in equation (2) or A in equation
(3). This operator is normally approximately ![]() full and,
therefore, a tractable operator to use for this method. As
such, the programming is implemented with a sparse matrix approach rather
than operators as it is traditional at SEP.
full and,
therefore, a tractable operator to use for this method. As
such, the programming is implemented with a sparse matrix approach rather
than operators as it is traditional at SEP.