Next: Applications of multi-dimensional spectral
Up: Spectral factorization
Previous: Spectral factorization
() describes the isomorphic process by which
multi-dimensional functions can be mapped into equivalent
one-dimensional functions.
The process depends on the concept of the helical boundary conditions,
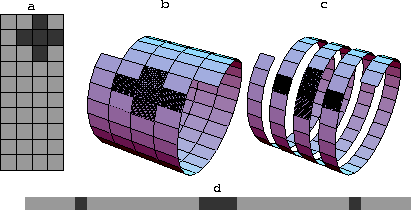
and is best illustrated by Figure 1.1, which shows a small
five-point filter on a two-dimensional space, being mapped into an
equivalent one-dimensional filter.
helix
Figure 1 Illustration of helical boundary
conditions mapping a two-dimensional function (a) onto a helix (b),
and then unwrapping the helix (c) into an equivalent one-dimensional
function (d). Figure by Sergey Fomel.

Under such a transformation, the concepts of causality and
minimum-phase become clear. One-dimensional spectral factorization
algorithms can be directly applied to the multi-dimensional helical
functions.





Next: Applications of multi-dimensional spectral
Up: Spectral factorization
Previous: Spectral factorization
Stanford Exploration Project
5/27/2001