




Next: REFERENCES
Up: SIGNAL-NOISE DECOMPOSITION BY DIP
Previous: The human eye as
Data 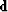 space can be decomposed into
known plus missing parts,
space can be decomposed into
known plus missing parts,
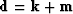 .We partition
an identity operator
.We partition
an identity operator 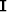 on the data space
into parts that separate the known from the missing data
on the data space
into parts that separate the known from the missing data
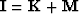 .Thus data space can be written as
.Thus data space can be written as
| 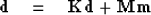 |
(17) |
where
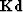 is zero-padded known data and
all the components of
is zero-padded known data and
all the components of 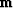 are freely adjustable.
are freely adjustable.
Data space 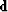 can also be decomposed into
signal plus noise,
can also be decomposed into
signal plus noise,
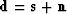 .Thus
.Thus
|  |
(18) |
Writing goals for signal and noise and then eliminating the noise
by the constraint equation (18) gives
| 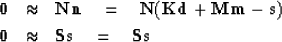 |
(19) |
| (20) |
Putting this in matrix form we have
the operator needed in computation
| ![\begin{displaymath}
\left[
\begin{array}
{c}
\bold 0 \\ \bold 0
\end{array...
...{c}
\bold N \bold K \bold d \\ \bold 0
\end{array} \right] \end{displaymath}](img54.gif) |
(21) |
I have not had time to prepare an example.





Next: REFERENCES
Up: SIGNAL-NOISE DECOMPOSITION BY DIP
Previous: The human eye as
Stanford Exploration Project
2/27/1998
![]() space can be decomposed into
known plus missing parts,
space can be decomposed into
known plus missing parts,
![]() .We partition
an identity operator
.We partition
an identity operator ![]() on the data space
into parts that separate the known from the missing data
on the data space
into parts that separate the known from the missing data
![]() .Thus data space can be written as
.Thus data space can be written as
![]() can also be decomposed into
signal plus noise,
can also be decomposed into
signal plus noise,
![]() .Thus
.Thus