




Next: Difficulty in higher dimensions
Up: FINITE DIFFERENCING
Previous: Solving tridiagonal simultaneous equations
The 45 diffraction equation differs from the 15
diffraction equation differs from the 15 equation
by the inclusion of a
equation
by the inclusion of a 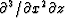 -derivative.
Luckily this derivative fits on the six-point differencing star
-derivative.
Luckily this derivative fits on the six-point differencing star
So other than modifying the six coefficients on the star,
it adds nothing to the computational cost.





Next: Difficulty in higher dimensions
Up: FINITE DIFFERENCING
Previous: Solving tridiagonal simultaneous equations
Stanford Exploration Project
10/31/1997
![]() diffraction equation differs from the 15
diffraction equation differs from the 15![]() equation
by the inclusion of a
equation
by the inclusion of a ![]() -derivative.
Luckily this derivative fits on the six-point differencing star
-derivative.
Luckily this derivative fits on the six-point differencing star