




Next: Percentiles and Hoare's algorithm
Up: Noisy data
Previous: Noisy data
Meanmeans, medians, and modes are different averages.
Given some data values di for i=1,2,...,N,
the arithmetic mean value m2 is
| 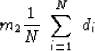 |
(1) |
It is useful to notice that this m2 is the solution
of the simple fitting problem
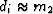 or
or
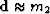 ,in other words,
,in other words, 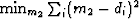 or
or
| 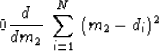 |
(2) |
The median of the di values
is found when the values are sorted from smallest to largest
and then the value in the middle is selected.
The median is delightfully well behaved even
if some of your data values happen to be near infinity.
Analytically,
the median arises from the optimization
| 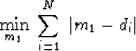 |
(3) |
To see why, notice that the derivative of the absolute value
function is the signum function,
| 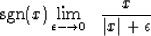 |
(4) |
The gradient vanishes at the minimum.
| 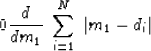 |
(5) |
The derivative is easy and the result is a sum of sgn() functions,
| 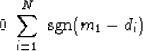 |
(6) |
In other words it is a sum of plus and minus ones.
If the sum is to vanish, the number of plus ones
must equal the number of minus ones.
Thus m1 is greater than half the data values and less than the other half,
which is the definition of a median.
The mean is said to minimize the  norm of the residual
and the median is said to minimize its
norm of the residual
and the median is said to minimize its 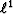 norm.
norm.
Before this chapter,
our model building was all based on the  norm.
The median is clearly a good idea
for data containing large bursts of noise,
but the median is a single value while geophysical models
are made from many unknown elements.
The
norm.
The median is clearly a good idea
for data containing large bursts of noise,
but the median is a single value while geophysical models
are made from many unknown elements.
The 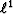 norm offers us the new opportunity
to build multiparameter models
where the data includes huge bursts of noise.
L-2 norm
L-1 norm
L-0 norm
norm offers us the new opportunity
to build multiparameter models
where the data includes huge bursts of noise.
L-2 norm
L-1 norm
L-0 norm
Yet another average is the ``mode,''
which is the most commonly occurring value.
For example, in the number sequence (1,1,2,3,5) the mode is 1
because it occurs the most times.
Mathematically, the mode minimizes the zero norm of the residual,
namely 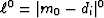 .To see why, notice that when we raise a residual to the zero power,
the result is 0 if di=m0, and it is 1 if
.To see why, notice that when we raise a residual to the zero power,
the result is 0 if di=m0, and it is 1 if 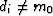 .Thus, the
.Thus, the 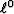 sum of the residuals
is the total number of residuals less those for which di matches m0.
The minimum of
sum of the residuals
is the total number of residuals less those for which di matches m0.
The minimum of 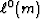 is the mode m=m0.
The zero power function is nondifferentiable at the place of interest so
we do not look at the gradient.
is the mode m=m0.
The zero power function is nondifferentiable at the place of interest so
we do not look at the gradient.
norms
Figure 1
Mean, median, and mode.
The coordinate is m.
Top is the  ,
, 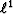 , and
, and 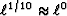 measures of m-1.
Bottom is the same measures of the data set (1,1,2,3,5).
(Made with Mathematica.)
measures of m-1.
Bottom is the same measures of the data set (1,1,2,3,5).
(Made with Mathematica.)





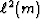 and
and
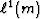 are convex functions of m (positive second derivative for all m),
and this fact leads to
the triangle inequalities
are convex functions of m (positive second derivative for all m),
and this fact leads to
the triangle inequalities 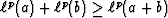 for
for 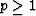 and assures slopes lead to a unique (if p>1) bottom.
Because there is no triangle inequality for
and assures slopes lead to a unique (if p>1) bottom.
Because there is no triangle inequality for 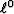 ,it should not be called a ``norm'' but a ``measure.''
,it should not be called a ``norm'' but a ``measure.''
Because most values are at the mode,
the mode is where a probability function is maximum.
The mode occurs with the maximum likelihood.
It is awkward to contemplate the mode for floating-point values
where the probability is minuscule (and irrelevant)
that any two values are identical.
A more natural concept is to think of the mode
as the bin containing the most values.
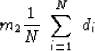
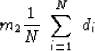
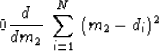
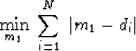
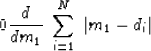
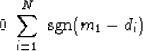
![]() norm.
The median is clearly a good idea
for data containing large bursts of noise,
but the median is a single value while geophysical models
are made from many unknown elements.
The
norm.
The median is clearly a good idea
for data containing large bursts of noise,
but the median is a single value while geophysical models
are made from many unknown elements.
The ![]() norm offers us the new opportunity
to build multiparameter models
where the data includes huge bursts of noise.
L-2 norm
L-1 norm
L-0 norm
norm offers us the new opportunity
to build multiparameter models
where the data includes huge bursts of noise.
L-2 norm
L-1 norm
L-0 norm
![]() .To see why, notice that when we raise a residual to the zero power,
the result is 0 if di=m0, and it is 1 if
.To see why, notice that when we raise a residual to the zero power,
the result is 0 if di=m0, and it is 1 if ![]() .Thus, the
.Thus, the ![]() sum of the residuals
is the total number of residuals less those for which di matches m0.
The minimum of
sum of the residuals
is the total number of residuals less those for which di matches m0.
The minimum of ![]() is the mode m=m0.
The zero power function is nondifferentiable at the place of interest so
we do not look at the gradient.
is the mode m=m0.
The zero power function is nondifferentiable at the place of interest so
we do not look at the gradient.

![]() and
and
![]() are convex functions of m (positive second derivative for all m),
and this fact leads to
the triangle inequalities
are convex functions of m (positive second derivative for all m),
and this fact leads to
the triangle inequalities ![]() for
for ![]() and assures slopes lead to a unique (if p>1) bottom.
Because there is no triangle inequality for
and assures slopes lead to a unique (if p>1) bottom.
Because there is no triangle inequality for ![]() ,it should not be called a ``norm'' but a ``measure.''
,it should not be called a ``norm'' but a ``measure.''