Next: GRADIENT ALONG THE BEDDING
Up: LOCAL MONOPLANE ANNIHILATOR
Previous: Crossing dips
Although the LOMOPLAN concept was developed for geophysical models,
not raw data,
initial experience showed that the LOMOPLAN program
is effective for quality testing data
and data interpretation.
Some field-data examples are in Figures ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) and
and ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
These results are not surprising.
A dominant local plane is removed,
and noise or the second-from-strongest local plane is left.
These data sets fit the local plane model so well
that subtracting the residual noise from the data made little improvement.
These figures are clearer on a video screen.
To facilitate examination of the residual on Figure
.
These results are not surprising.
A dominant local plane is removed,
and noise or the second-from-strongest local plane is left.
These data sets fit the local plane model so well
that subtracting the residual noise from the data made little improvement.
These figures are clearer on a video screen.
To facilitate examination of the residual on Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) on paper
(which has a lesser dynamic range than video),
I recolored the white residual with a short triangle filter on the time axis.
on paper
(which has a lesser dynamic range than video),
I recolored the white residual with a short triangle filter on the time axis.
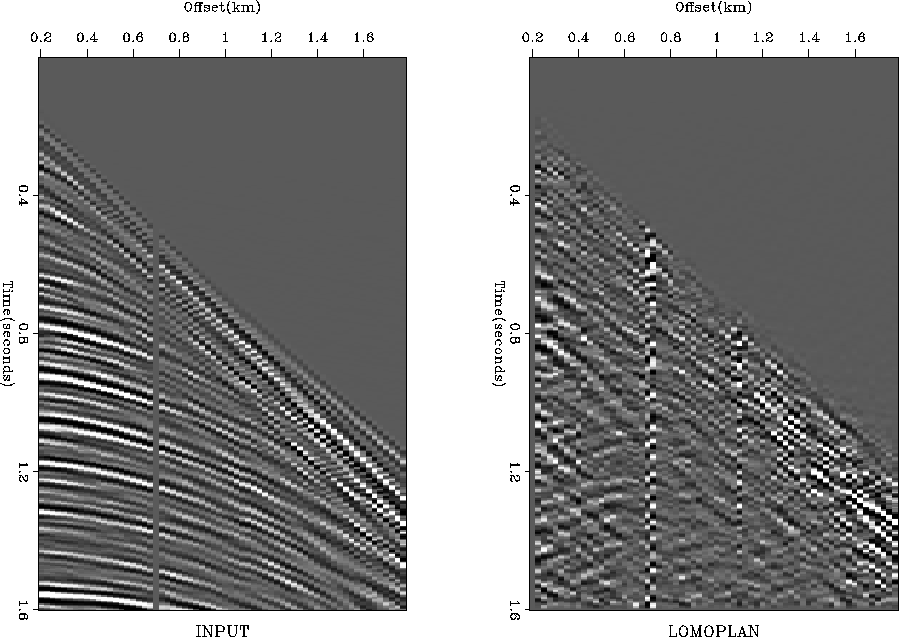
dgulf90
Figure 6
Data section from the Gulf of Mexico (left)
and after LOMOPLAN (right)
Press button for movie.





The residual in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) is large at the dead trace
and wherever the data contains crossing events.
Also, closer examination showed that the strong residual trace
near 1.1 km offset is apparently slightly time-shifted,
almost certainly a cable problem,
perhaps resulting from a combination of the stepout and a few dead pickups.
Overall, the local-plane residual shows a low-frequency water-velocity wave
seeming to originate from the ship.
is large at the dead trace
and wherever the data contains crossing events.
Also, closer examination showed that the strong residual trace
near 1.1 km offset is apparently slightly time-shifted,
almost certainly a cable problem,
perhaps resulting from a combination of the stepout and a few dead pickups.
Overall, the local-plane residual shows a low-frequency water-velocity wave
seeming to originate from the ship.
yc2790
Figure 7
Portion of Yilmaz and Cumro data set 27 (left)
and after LOMOPLAN (right).
Press button for movie.










Next: GRADIENT ALONG THE BEDDING
Up: LOCAL MONOPLANE ANNIHILATOR
Previous: Crossing dips
Stanford Exploration Project
4/27/2004
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) and
and ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
These results are not surprising.
A dominant local plane is removed,
and noise or the second-from-strongest local plane is left.
These data sets fit the local plane model so well
that subtracting the residual noise from the data made little improvement.
These figures are clearer on a video screen.
To facilitate examination of the residual on Figure
.
These results are not surprising.
A dominant local plane is removed,
and noise or the second-from-strongest local plane is left.
These data sets fit the local plane model so well
that subtracting the residual noise from the data made little improvement.
These figures are clearer on a video screen.
To facilitate examination of the residual on Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) on paper
(which has a lesser dynamic range than video),
I recolored the white residual with a short triangle filter on the time axis.
on paper
(which has a lesser dynamic range than video),
I recolored the white residual with a short triangle filter on the time axis.