




Next: Observation of dispersive waves
Up: PHASE DELAY AND GROUP
Previous: Group delay
We will see that the group delay of a filter P
is a simple function of the Fourier transform of the filter.
I have named the filter P
to remind us that the theorem strictly applies only
to all-pass filters,
though in practice a bit of energy absorption might be OK.
The phase angle 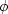 could be computed as the arctangent of the ratio
of imaginary to real parts of the Fourier transform,
namely,
could be computed as the arctangent of the ratio
of imaginary to real parts of the Fourier transform,
namely, ![$\phi(\omega) = \arctan [ \Im P(\omega)/ \Re P(\omega)]$](img100.gif) .As with (12), we use
.As with (12), we use
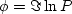 ;and from (33) we get
;and from (33) we get
| 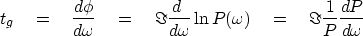 |
(33) |
which could be expressed as the Fourier dual to
equation (14).





Next: Observation of dispersive waves
Up: PHASE DELAY AND GROUP
Previous: Group delay
Stanford Exploration Project
10/21/1998