




Next: MATRICES AND VECTORS
Up: Notation
Previous: SCALARS
The example x(t), xt, Xk, X(Z), 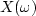 can be understood as follows.
A lower-case letter with a function argument (t)
denotes a continuous time function (rare).
Lower case with a subscript denotes a signal or filter
as a function of discrete time (common).
Upper case with subscript denotes a discrete Fourier transform.
Z-transforms are denoted by the function argument (Z).
Where a function argument
can be understood as follows.
A lower-case letter with a function argument (t)
denotes a continuous time function (rare).
Lower case with a subscript denotes a signal or filter
as a function of discrete time (common).
Upper case with subscript denotes a discrete Fourier transform.
Z-transforms are denoted by the function argument (Z).
Where a function argument  is occasionally seen,
such as in
is occasionally seen,
such as in 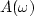 ,it is generally a shorthand for
,it is generally a shorthand for 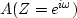 .For a definition of the complex conjugate of filters,
see page
.For a definition of the complex conjugate of filters,
see page ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
.
aA feedback filter (autoregression)
bB convolution filter
cC causal filter; reflected wave; cross-spectrum
dD downgoing wave
E escaping wave
fF component of layer matrix; force; generic function
gG component of layer matrix; analytic signal; causal garbage filter
hH admittance
I causal integration operator
JKLMO unused
N noise
pP phase shift; pressure; all-pass filter; generic input space
qQ quadrature filter; generic output space
rR impedance; reflection seismogram
sS S is spectrum; st is autocorrelation
T transmitted wave
uU upcoming wave; logarithm of S
vV velocity
W weighting function; vertical component of flow
xX generic input signal
yY generic output signal
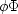 phase
phase





Next: MATRICES AND VECTORS
Up: Notation
Previous: SCALARS
Stanford Exploration Project
10/21/1998
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
.
phase