




Next: Acoustic wave-equation in 3D
Up: Shragge: GRWE
Previous: Introduction
Geometry in a generalized 3D Riemannian space is described by a symmetric
metric tensor, gij=gji, that relates the geometry in a
non-orthogonal coordinate system, 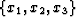 , to an underlying
Cartesian mesh,
, to an underlying
Cartesian mesh, 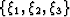 Guggenheimer (1977). In
matrix form, the metric tensor is written,
Guggenheimer (1977). In
matrix form, the metric tensor is written,
| ![\begin{displaymath}
\left[g_{ij}\right]
=
\left[\begin{array}
{ccc}
g_{11} & g...
...g_{22} & g_{23} \ g_{13} & g_{23} & g_{33} \end{array}\right],\end{displaymath}](img3.gif) |
(1) |
where g11, g12, g22, g13, g23 and 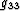 are functions
linking the two coordinate systems through,
are functions
linking the two coordinate systems through,
| 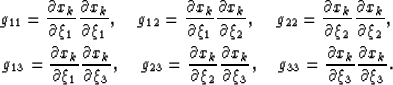 |
|
| (2) |
(Summation notation - gii = g11+g22+g33 - is used in
equations throughout this paper.) The associated (or inverse) metric
tensor, gij, is defined by 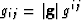 , where
, where
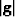 is metric tensor matrix determinant. The associated
metric tensor is given by,
is metric tensor matrix determinant. The associated
metric tensor is given by,
| ![\begin{displaymath}
\left[g^{ij}\right] =\frac{1}{\left\vert\mathbf{g}\right\ve...
..._{13}-g_{11}g_{23}& g_{11}g_{22}-g_{12}^2
\end{array}\right],\end{displaymath}](img8.gif) |
(3) |
and has the following metric determinant,
| ![\begin{displaymath}
\vert\mathbf{g}\vert = \AA\,(g_{11}g_{22}-g_{12}^2)\, \left...
...13}^2-2g_{12}g_{23}g_{13}}{\AA(g_{11}g_{22}-g_{12}^2)} \right].\end{displaymath}](img9.gif) |
(4) |
Weighted metric tensor, 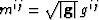 , is a useful
definition for the following development.
, is a useful
definition for the following development.





Next: Acoustic wave-equation in 3D
Up: Shragge: GRWE
Previous: Introduction
Stanford Exploration Project
4/5/2006
![\begin{displaymath}
\left[g_{ij}\right]
=
\left[\begin{array}
{ccc}
g_{11} & g...
...g_{22} & g_{23} \ g_{13} & g_{23} & g_{33} \end{array}\right],\end{displaymath}](img3.gif)
![\begin{displaymath}
\left[g_{ij}\right]
=
\left[\begin{array}
{ccc}
g_{11} & g...
...g_{22} & g_{23} \ g_{13} & g_{23} & g_{33} \end{array}\right],\end{displaymath}](img3.gif)
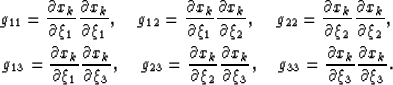
![\begin{displaymath}
\left[g^{ij}\right] =\frac{1}{\left\vert\mathbf{g}\right\ve...
..._{13}-g_{11}g_{23}& g_{11}g_{22}-g_{12}^2
\end{array}\right],\end{displaymath}](img8.gif)