Next: Estimating Wij from cross-well
Up: EXAMPLES
Previous: Estimating Wij from VSP
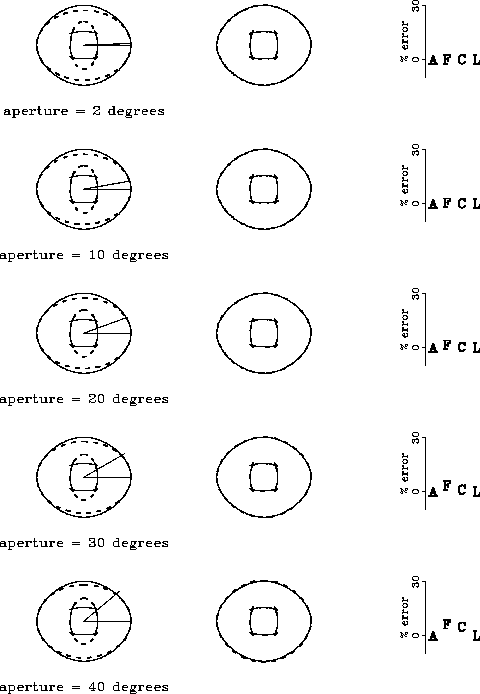
Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) shows how the horizontal double elliptic
approximation works for different ray angles measured from the
horizontal. When comparing this case with the VSP case
(Figure
shows how the horizontal double elliptic
approximation works for different ray angles measured from the
horizontal. When comparing this case with the VSP case
(Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ), we see that the approximation works better
for ray angles around the horizontal than around the vertical,
even when the angles are large. The estimated impulse
responses agree well with the given ones, and the errors
in the elastic constants are negligible for angles
less of fewer than 30 degrees.
), we see that the approximation works better
for ray angles around the horizontal than around the vertical,
even when the angles are large. The estimated impulse
responses agree well with the given ones, and the errors
in the elastic constants are negligible for angles
less of fewer than 30 degrees.
xw
Figure 3 Left: impulse response for P- and SV-waves (continuous lines)
compared with their
elliptical approximations around the vertical (dashed lines). Center:
given impulse responses (continuous) compared to the ones
calculated from the estimated elastic
constants (dashed). Right: absolute value of the error made
in the estimation of the elastic constants when using
the horizontal double elliptic approximation.
The elastic constants are A = W11, F = W13,
C = W33, and L = W44.

The reason why the horizontal double elliptic approximation
works better than the vertical double elliptic
approximation
is that the elliptical approximation
for P-wave impulse response is more adequate at larger angles
around the horizontal than around the vertical, where
the group velocity is lower. Notice that the elliptic approximations
around the vertical are almost circular.
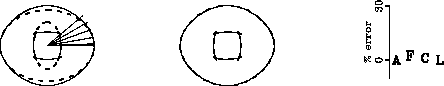
Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) shows that
when small and large ray angles are used simultaneously to calculate
the elliptical approximations around the horizontal,
the result is roughly an average of the results shown in
Figure
shows that
when small and large ray angles are used simultaneously to calculate
the elliptical approximations around the horizontal,
the result is roughly an average of the results shown in
Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) . The
agreement between given and estimated impulse responses
is excellent and the error in the estimation of the elastic
constants is
. The
agreement between given and estimated impulse responses
is excellent and the error in the estimation of the elastic
constants is 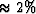 for W13 (F) and
for W13 (F) and 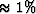 for W33 (C).
for W33 (C).
xw-4angles
Figure 4 Left: impulse response for P- and SV-waves (continuous lines)
compared with their
elliptical approximations around the vertical (dashed lines).
All ray angles shown are used simultaneously to
calculate the elliptical approximations. Center:
given impulse responses (continuous) compared to the ones
calculated from the estimated elastic
constants (dashed). Right: absolute value of the error made
in the estimation of the elastic constants when using
the horizontal double elliptic approximation.
The elastic constants are A = W11, F = W13,
C = W33, and L = W44.






Next: Estimating Wij from cross-well
Up: EXAMPLES
Previous: Estimating Wij from VSP
Stanford Exploration Project
11/17/1997
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) shows how the horizontal double elliptic
approximation works for different ray angles measured from the
horizontal. When comparing this case with the VSP case
(Figure
shows how the horizontal double elliptic
approximation works for different ray angles measured from the
horizontal. When comparing this case with the VSP case
(Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ), we see that the approximation works better
for ray angles around the horizontal than around the vertical,
even when the angles are large. The estimated impulse
responses agree well with the given ones, and the errors
in the elastic constants are negligible for angles
less of fewer than 30 degrees.
), we see that the approximation works better
for ray angles around the horizontal than around the vertical,
even when the angles are large. The estimated impulse
responses agree well with the given ones, and the errors
in the elastic constants are negligible for angles
less of fewer than 30 degrees.