Next: About this document ...
Up: Lumley: Green's function traveltime
Previous: Acknowledgments
-
Cabrera, J., J., Perkins, W. T., Ratcliff, D. W., and Lynn, W., 1992,
3-D prestack depth migration on a massively parallel computer:
implementation and case history: 54th Mtg. Eur. Assoc. Expl.
Geophys., Abstracts, 268-269.
-
Cervený, V., Molotkov, I. A., and Psencík, I., 1977, Ray method in
seismology: Univerzita Karlova, Praha.
-
Beydoun, W. B., and Keho, T. H., 1987, The paraxial ray method:
Geophysics, 52, 1639-1653.
-
Keho, T. H., and Beydoun, W. B., 1988, Paraxial ray Kirchhoff migration:
Geophysics, 53, 1540-1546.
-
Luo, Y., and Schuster, G. T., 1990, Wave-equation traveltime inversion:
60th Annual Internat. Mtg., Soc. Expl. Geophys., Expanded Abstracts,
1207-1210.
-
Strang, G., 1980, Linear algebra and its applications: Academic Press.
-
Van Trier, J., 1991, A massively parallel implementation of prestack Kirchhoff
depth migration: 53rd Mtg. Eur. Assoc. Expl. Geophys., Abstracts.
-
Van Trier, J., and Symes, W. W., 1991, Upwind finite-difference calculation
of traveltimes: Geophysics, 56, 812-821.
-
Vidale, J. E., 1988, Finite-difference calculation of traveltimes:
Bull. Seis. Soc. Am., 78, 2062-2076.
-
Zhang, L., 1992, Wavefront propagation by local ray-tracing: this report.
marmousi
Figure 12 Marmousi 2-D velocity model.
Top panel is original velocity model, lower panel is a smoothed
version using a pyramid of base half-width equal to 80 m, which
is used for the traveltime and interpolation calculations.




 m13t
m13t
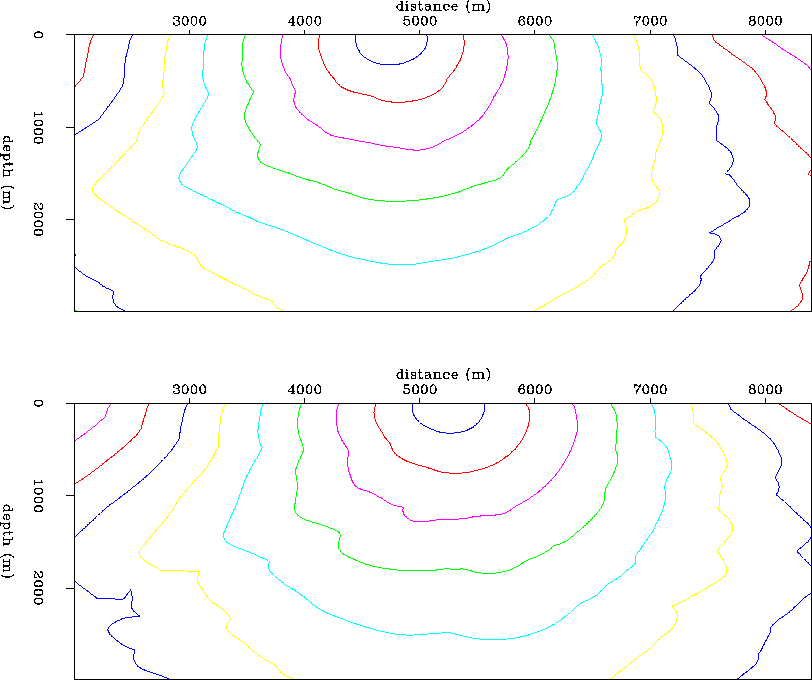
Figure 13 Marmousi velocity model.
Contours of traveltime field for
the two given surface source positions at 4.75 km (top) and 5.25 km
(bottom).




 m1xz
m1xz
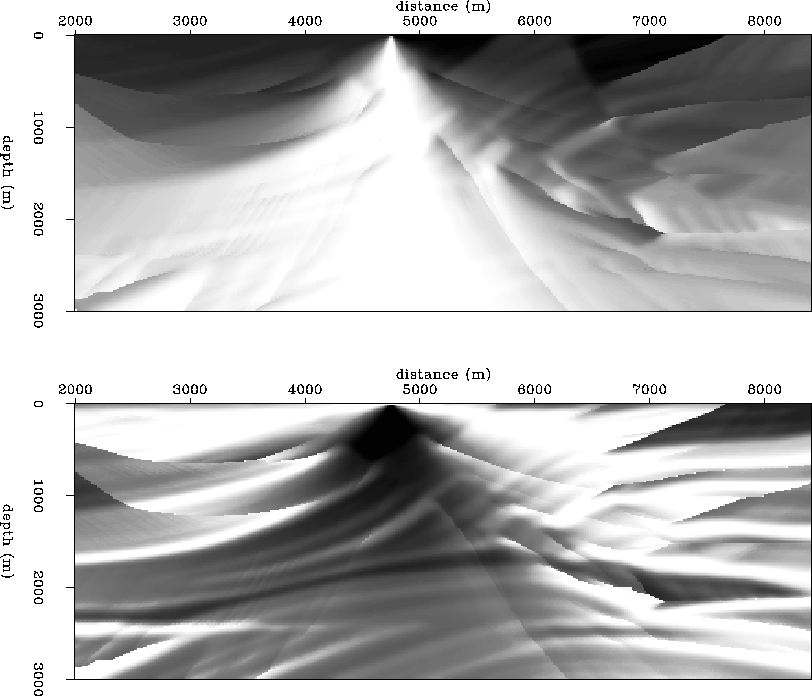
Figure 14 Marmousi velocity model.
Horizontal (top) and vertical
(bottom) traveltime gradient fields for
the surface source positioned at 4.75 km.




 m3xz
m3xz
Figure 15 Marmousi velocity model.
Horizontal (top) and vertical
(bottom) traveltime gradient fields for
the surface source positioned at 5.25 km.




 mite
mite
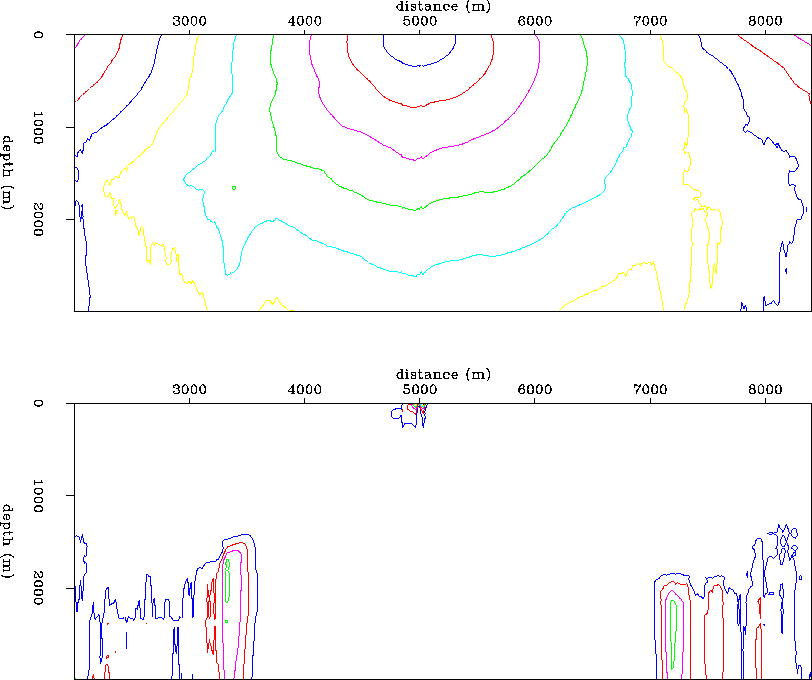
Figure 16 Marmousi velocity model.
Interpolated traveltime field.
The top panel is the interpolated traveltime field for a surface
source positioned at 5.00 km. The lower panel is the relative
error between the interpolated traveltime field, and the correct
traveltimes modeled by finite differencing the eikonal. The
contour farthest from the source region is at 5% relative error,
and the contour values increase to 50% error right at the source
location, in 5% contour increments.




 mixz
mixz
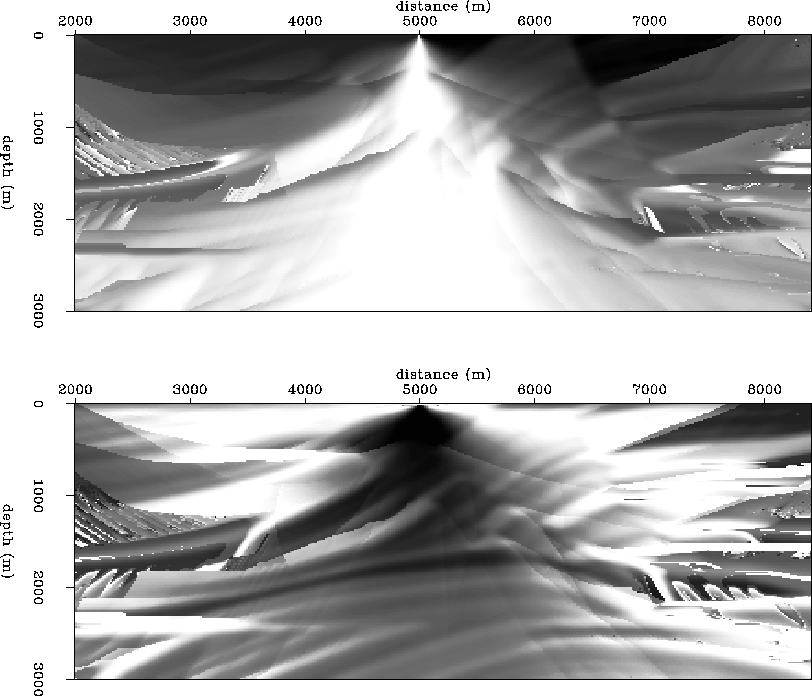
Figure 17 Marmousi velocity model.
Horizontal (top) and vertical
(bottom) traveltime gradient fields for
the interpolated surface source positioned at 5.00 km.










Next: About this document ...
Up: Lumley: Green's function traveltime
Previous: Acknowledgments
Stanford Exploration Project
11/17/1997