




Next: S-S reflection coefficient
Up: IMAGING CONDITION
Previous: P-P reflection coefficient
Similarly, a pure Sv shear mode can be described by the curl of a vector
potential. To isolate the shear wave it is enough to apply a curl
operator to the displacement field.
| 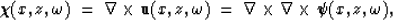 |
(3) |
For this 2-D implementation the wavefields are invariant in the
direction of the unit vector normal to the experiment plane (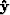 ).
As a result, the only non vanishing component of
).
As a result, the only non vanishing component of 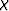 will be in
the
will be in
the 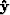 direction. Defining
direction. Defining
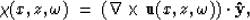
and using the same approach used for P-P, results in the following
equation to describe the imaging condition for the P-S reflection coefficient
| 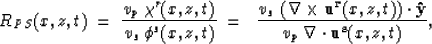 |
(4) |
and for the S-P reflection coefficient
| 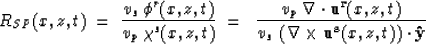 |
(5) |





Next: S-S reflection coefficient
Up: IMAGING CONDITION
Previous: P-P reflection coefficient
Stanford Exploration Project
11/18/1997
![]() ).
As a result, the only non vanishing component of
).
As a result, the only non vanishing component of ![]() will be in
the
will be in
the ![]() direction. Defining
direction. Defining
![]()