|
|
|
|
Correlation energy between surface and borehole stations at the Valhall field |
Tests of the practicality of passive seismic interferometry for these purposes has been ongoing with ambient seismic noise data provided by the permanent ocean-bottom cable (OBC) array at the Valhall field. Artman (2007) and Landes et al. (2009) showed that virtual omnidirectional point sources could not be captured at frequencies typical of seismic exploration (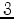 -
-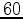 Hz). Later, de Ridder and Dellinger (2011) showed that virtual low-frequency (
Hz). Later, de Ridder and Dellinger (2011) showed that virtual low-frequency (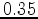 -
-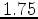 Hz), omnidirectional Scholte waves along the ocean floor could be generated from seismic noise. They were able to use the Scholte-wave travel-time information for tomographic imaging of structures in the near-surface (0
-
Hz), omnidirectional Scholte waves along the ocean floor could be generated from seismic noise. They were able to use the Scholte-wave travel-time information for tomographic imaging of structures in the near-surface (0
-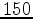 m).
m).
In previous studies of passive seismic interferometry for seismic exploration at the Valhall field (de Ridder and Dellinger, 2011; Artman, 2007; Bussat and Kugler, 2009) correlations were performed between stations on the ocean floor. In this study we correlate ambient seismic noise recorded over the same time period by the OBC array and by five downhole stations at nearly 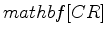 km depth. Our goal is to test whether Green's functions can be extracted between the borehole stations and the surface stations. In this report, we present the results for low frequencies (
km depth. Our goal is to test whether Green's functions can be extracted between the borehole stations and the surface stations. In this report, we present the results for low frequencies (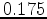 -
-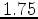 Hz).
Hz).
|
|
|
|
Correlation energy between surface and borehole stations at the Valhall field |