 |
 |
 |
 | Velocity model evaluation through Born modeling and migration: a feasibility study |  |
![[pdf]](icons/pdf.png) |
Next: Generalized source function
Up: Halpert and Tang: Fast
Previous: Introduction
The goal of the procedure we will describe is to use Born modeling to synthesize a new dataset that is much smaller than the original dataset used to generate an initial migrated image. Since the synthesized data can be ``recorded'' at any location in  ,
, 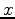 , and even
, and even 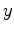 , this procedure is effectively target-oriented. There are three basic steps needed to reach our goal of efficient velocity model evaluation:
, this procedure is effectively target-oriented. There are three basic steps needed to reach our goal of efficient velocity model evaluation:
- Generate an areal source function using one or more subsurface offset gathers from the initial prestack image.
- Using the new source function and a reflectivity model based on the initial image, employ Born modeling to generate a new dataset with acquisition geometry best suited to image the target area.
- Migrate the simulated data obtained in Step 2, using the source function from Step 1. This step is extremely computationally efficient compared to a full migration of the original data, allowing for testing of several possible velocity models in a fraction of the time it would take to evaluate them using standard migration techniques.
In the following sections we detail the theoretical basis for each of these steps.
Subsections
 |
 |
 |
 | Velocity model evaluation through Born modeling and migration: a feasibility study |  |
![[pdf]](icons/pdf.png) |
Next: Generalized source function
Up: Halpert and Tang: Fast
Previous: Introduction
2011-09-13
![]() ,
, ![]() , and even
, and even ![]() , this procedure is effectively target-oriented. There are three basic steps needed to reach our goal of efficient velocity model evaluation:
, this procedure is effectively target-oriented. There are three basic steps needed to reach our goal of efficient velocity model evaluation: