|
plane3D.fft_no_mirr.flat_cos
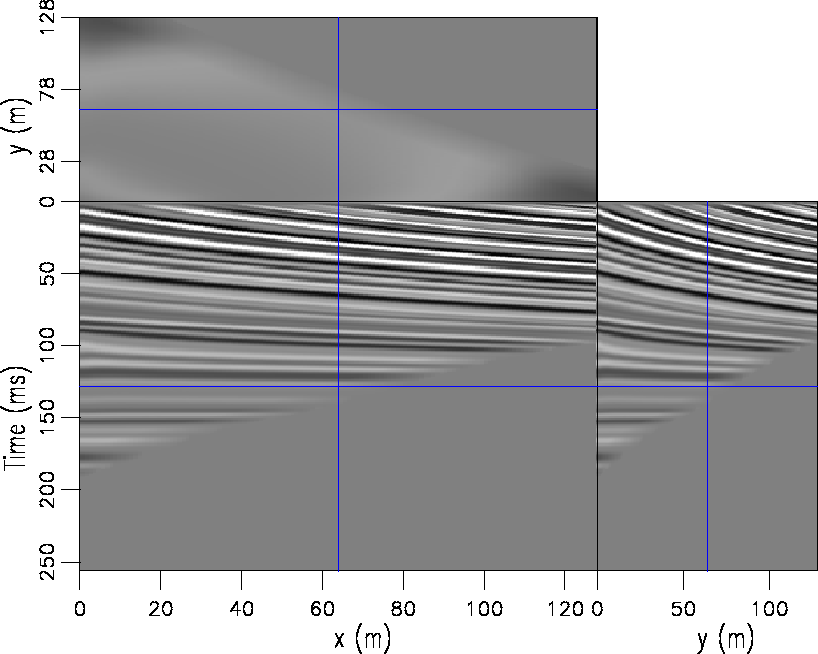
Figure 3 The data in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) flattened using the FFT method without mirrors. flattened using the FFT method without mirrors.
|  |
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) . Although it is just a simple model, it still requires mirroring boundary conditions for the FFT method because the divergence of the dip (
. Although it is just a simple model, it still requires mirroring boundary conditions for the FFT method because the divergence of the dip (![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) . Notice it is perfectly flat. If we apply the same FFT algorithm without mirrors, we get the result displayed in Figure
. Notice it is perfectly flat. If we apply the same FFT algorithm without mirrors, we get the result displayed in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) . It is clearly not flat. If we apply the DCT method as shown in Figure
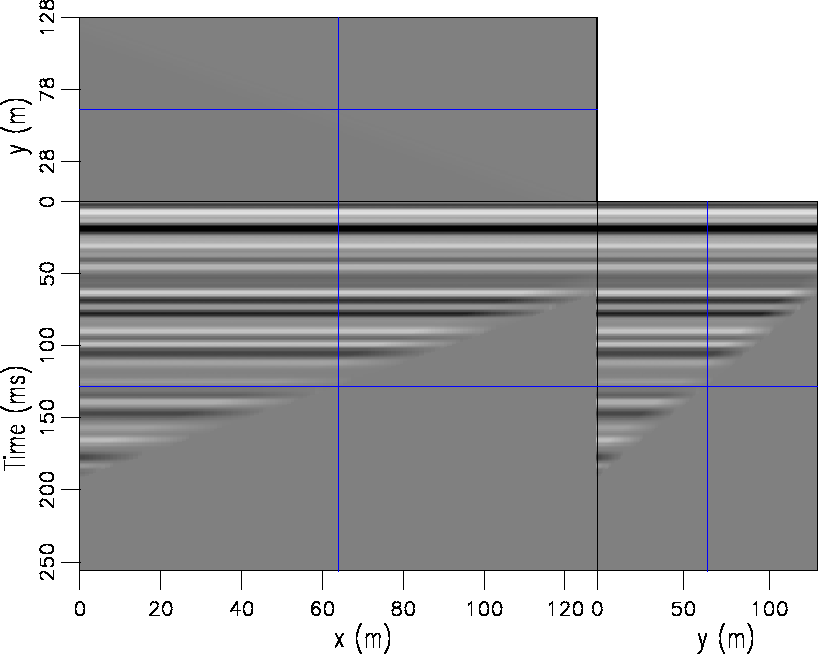
. It is clearly not flat. If we apply the DCT method as shown in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) , it is flattened in one iteration using only a fraction of the memory and computations.
, it is flattened in one iteration using only a fraction of the memory and computations.
|
plane3D.fft_no_mirr.flat_cos
Figure 3 The data in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) flattened using the FFT method without mirrors. flattened using the FFT method without mirrors.
|  |
|
plane3D.cos.flat_cos
Figure 4 The data in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) flattened using the DCT method without mirrors. flattened using the DCT method without mirrors.
|  |