




Next: Numerical examples
Up: Shan: Implicit migration for
Previous: Table-driven implicit finite-difference migration
In the 3D case, as in the isotropic migration, the dispersion relation is split into x and y components as follows:
| ![\begin{displaymath}
\frac{\partial}{\partial z}P=i\frac{\omega}{v_p}\left [ \fra...
...frac{v_p^2}{\omega^2}\frac{\partial^2}{\partial y^2}}\right ]P.\end{displaymath}](img47.gif) |
(13) |
This two-way splitting causes numerical anisotropy, which can be remedied by a phase-correction filter Li (1991) in
the Fourier domain as follows:
| 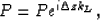 |
(14) |
where
| ![\begin{displaymath}
k_L=\sqrt{\frac{1-(1+2\varepsilon_r)\frac{k_r^2}{(\omega/v_p...
...{v_p^r}k_y)^2}{1-\beta_1^r(\frac{\omega}{v_p^r}k_y)^2}\right ],\end{displaymath}](img49.gif) |
(15) |
where vpr is the reference vertical velocity, 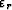 and
and 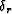 are the reference anisotropy parameters, and
are the reference anisotropy parameters, and 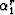 and
and 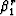 are the optimized finite-difference coefficients corresponding to the anisotropy parameters
are the optimized finite-difference coefficients corresponding to the anisotropy parameters 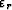 and
and 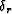 .
.





Next: Numerical examples
Up: Shan: Implicit migration for
Previous: Table-driven implicit finite-difference migration
Stanford Exploration Project
4/5/2006
![\begin{displaymath}
\frac{\partial}{\partial z}P=i\frac{\omega}{v_p}\left [ \fra...
...frac{v_p^2}{\omega^2}\frac{\partial^2}{\partial y^2}}\right ]P.\end{displaymath}](img47.gif)
![\begin{displaymath}
\frac{\partial}{\partial z}P=i\frac{\omega}{v_p}\left [ \fra...
...frac{v_p^2}{\omega^2}\frac{\partial^2}{\partial y^2}}\right ]P.\end{displaymath}](img47.gif)
![\begin{displaymath}
k_L=\sqrt{\frac{1-(1+2\varepsilon_r)\frac{k_r^2}{(\omega/v_p...
...{v_p^r}k_y)^2}{1-\beta_1^r(\frac{\omega}{v_p^r}k_y)^2}\right ],\end{displaymath}](img49.gif)