|
rayprim
Figure 1 Construction of the primary reflection from a dipping interface. |  |
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
.
|
rayprim
Figure 1 Construction of the primary reflection from a dipping interface. |  |
The moveout of the primary reflection in the CMP domain is given by:
| |
(1) |
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
.
The raypath of the multiple reflection can be considered as a cascaded of two
primary reflections as SRME methods do
(Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ), but the
traveltime of the multiple, tm, can be computed more easily as the traveltime of
an equivalent primary from a reflector dipping at twice the dip angle of the
actual reflector as illustrated in Figure
), but the
traveltime of the multiple, tm, can be computed more easily as the traveltime of
an equivalent primary from a reflector dipping at twice the dip angle of the
actual reflector as illustrated in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) . That is,
. That is,
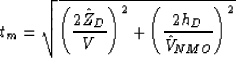 |
(2) |
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) corresponds to a CMP showing
the primary and the multiple reflection. Obviously, they are both hyperbolas
since the multiple has the same kinematics as a primary from a reflector
dipping at twice the dip as indicated above.
corresponds to a CMP showing
the primary and the multiple reflection. Obviously, they are both hyperbolas
since the multiple has the same kinematics as a primary from a reflector
dipping at twice the dip as indicated above.
|
raymul1
Figure 2 Decomposition of the water-bottom multiple as a cascaded of two primary reflections. | 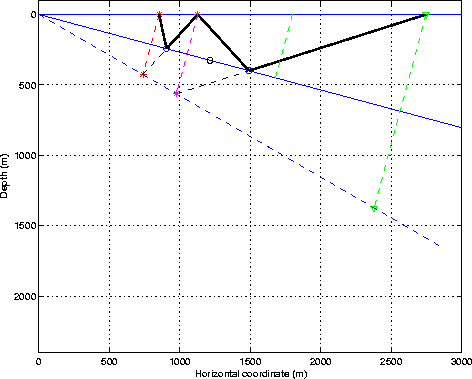 |
|
raymul2
Figure 3 Multiple reflection as a primary from an equivalent reflector with twice the dip angle. |  |
|
moveouts1
Figure 4 Moveout curves of primary and water-bottom multiple from a dipping interface on a CMP gather. | 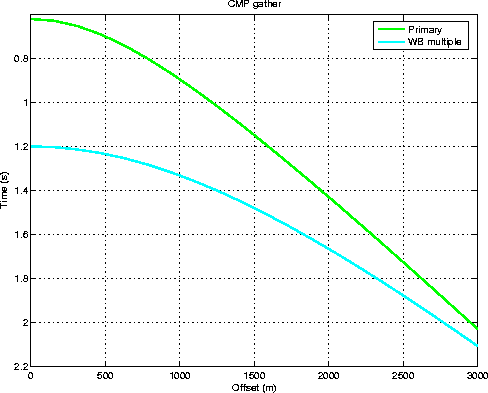 |