




Next: - downward extrapolation
Up: Alvarez and Artman: Wavefield
Previous: Introduction
In this section, we will briefly review, from the mathematical point of
view, the 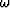 -
- -
- 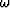 -
-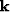 algorithm.
This will serve as the starting point for the presentation of the new
extrapolation method in the next section.
algorithm.
This will serve as the starting point for the presentation of the new
extrapolation method in the next section.
Let 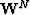 be the wavefield at depth step N in the
be the wavefield at depth step N in the
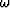 -
-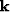 domain and let
domain and let 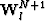 be the wavefield extrapolated from
depth step N to depth step N+1 using reference velocity Vl.
That is:
be the wavefield extrapolated from
depth step N to depth step N+1 using reference velocity Vl.
That is:
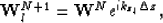
where 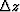 is the depth of the Nth layer and kzl is given by the
dispersion relation:
is the depth of the Nth layer and kzl is given by the
dispersion relation:
| 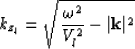 |
(1) |
with 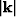 being the magnitude of the horizontal wavenumber vector.
PSPI handles the difference between the true velocity and the
reference velocity by interpolating the downward-continued wavefields in
the
being the magnitude of the horizontal wavenumber vector.
PSPI handles the difference between the true velocity and the
reference velocity by interpolating the downward-continued wavefields in
the 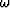 -
- domain based on the difference between the reference
velocities and the model velocity at each
domain based on the difference between the reference
velocities and the model velocity at each  position. The
interpolated wavefield is therefore given by:
position. The
interpolated wavefield is therefore given by:
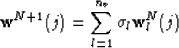
where 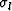 is an interpolation factor (
is an interpolation factor (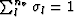 ),
),
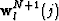 is the downward-continued wavefield in the
is the downward-continued wavefield in the
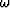 -
- domain at the spatial location j, and nv is the
number of reference velocities.
domain at the spatial location j, and nv is the
number of reference velocities.
Extended split-step adds a correction before the
interpolation, the so-called ``thin lens term'':
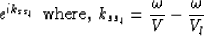
where V is the true model velocity. Depending on the choice and number of
reference velocities, split-step can make significant improvements in accuracy
compared to PSPI.
Other methods, such as
pseudo-screen and Fourier finite-difference, increase the accuracy of the
result by adding high-order spatial derivatives to the computation of
the kzl term Biondi (2004); Huang et al. (1999); Ristow and Ruhl (1994); Xie and Wu (1999). The more
accurate approximation of kzl relaxes the need for a large number
of reference velocities such that with fewer reference velocities similar or
even better accuracies can be obtained compared with split-step.
The last step in either of these methods is to Fourier transform the
interpolated wavefield to the 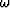 -
-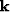 space. This wavefield will
then be the input to the propagation at the next depth step.
space. This wavefield will
then be the input to the propagation at the next depth step.
It should be clear that the accuracy of these methods, especially PSPI
and extended split-step, is directly related to the
accuracy of the wavefield interpolation and the number and choice of
the reference velocities.





Next: - downward extrapolation
Up: Alvarez and Artman: Wavefield
Previous: Introduction
Stanford Exploration Project
5/3/2005
![]() be the wavefield at depth step N in the
be the wavefield at depth step N in the
![]() -
-![]() domain and let
domain and let ![]() be the wavefield extrapolated from
depth step N to depth step N+1 using reference velocity Vl.
That is:
be the wavefield extrapolated from
depth step N to depth step N+1 using reference velocity Vl.
That is:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() -
-![]() space. This wavefield will
then be the input to the propagation at the next depth step.
space. This wavefield will
then be the input to the propagation at the next depth step.