




Next: Causality and the unit
Up: INSTABILITY
Previous: The meaning of divergence
Given different numerical values for Z, we can ask
whether X(Z) is finite or infinite.
Numerical values of Z of particular interest are
Z = +1, Z = -1, and
all those complex values of Z which are unit magnitude,
say |Z| = 1 or 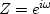 ,where
,where  is the real Fourier transform variable.
When
is the real Fourier transform variable.
When  is the variable, the Z-transform is a Fourier sum.
is the variable, the Z-transform is a Fourier sum.
We can restrict our attention to those signals ut
that have a finite
amount of energy by demanding that U(Z) be
finite for all values of Z on the unit circle |Z| = 1.
Filter functions always have finite energy.





Next: Causality and the unit
Up: INSTABILITY
Previous: The meaning of divergence
Stanford Exploration Project
10/21/1998