




Next: References
Up: DMO BY FOURIER TRANSFORM
Previous: Zhang's improved DMO
Both Hale and Zhang separate the NMO correction from the DMO
correction. However for variable velocity media this can not
be done, and in order to generalize the 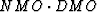 operation
we have to use the migration to zero-offset (MZO) concept.
Migration to zero-offset is the process that transforms a
nonzero-offset (constant offset) section into a zero-offset
section. In constant velocity media
operation
we have to use the migration to zero-offset (MZO) concept.
Migration to zero-offset is the process that transforms a
nonzero-offset (constant offset) section into a zero-offset
section. In constant velocity media 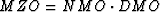 .The Fourier transform expression is simply obtained by using
again equation (20) without separating the NMO step.
We have
.The Fourier transform expression is simply obtained by using
again equation (20) without separating the NMO step.
We have
| 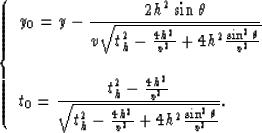 |
(25) |
The differentials of the new variables are
| 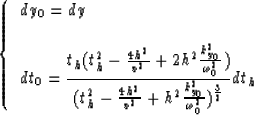 |
(26) |
After replacing the variables y0 and t0 in equation (21)
we obtain
| 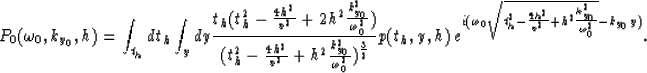 |
(27) |
Note that if we replace the quantity
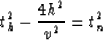
in equation (27) we get the same phase as the one obtained
by Hale and Zhang, but the Jacobian differs from Zhang's Jacobian
by a factor
| 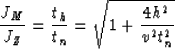 |
(28) |
which corresponds to the Jacobian of the NMO transformation.





Next: References
Up: DMO BY FOURIER TRANSFORM
Previous: Zhang's improved DMO
Stanford Exploration Project
11/17/1997
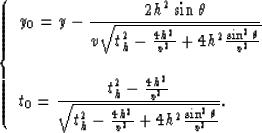
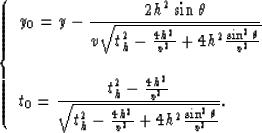
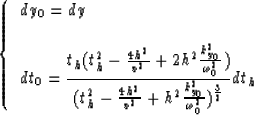
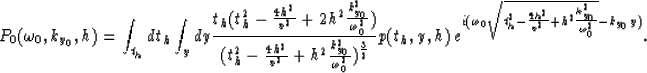
![]()