Next: CONCLUSIONS
Up: THE SPLIT-STEP FOURIER MODELING
Previous: A 2-D example
The three dimensional model is built for a linearly varying velocity
in all three coordinates: v(x,y,z)=v0+ax+by+cz.
The reflection model is just a diffractor situated inside the velocity cube.
The size of the modeling baby-grid (64x64x256) was imposed by the amount of
memory available on the SEP Connection Machine. The size
of the available memory is also the reason why
I have not implemented absorbing boundaries for the 3-D
algorithm. With
20 gridpoints on each side of the 64 points mesh the active area
will be only 24 points!
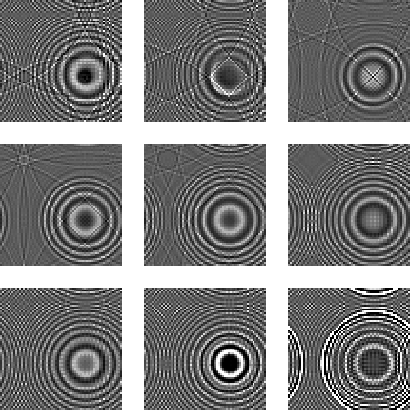
Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) displays time slices through the 3-D cube
of diffraction data obtained using PSPI modeling while
Figure
displays time slices through the 3-D cube
of diffraction data obtained using PSPI modeling while
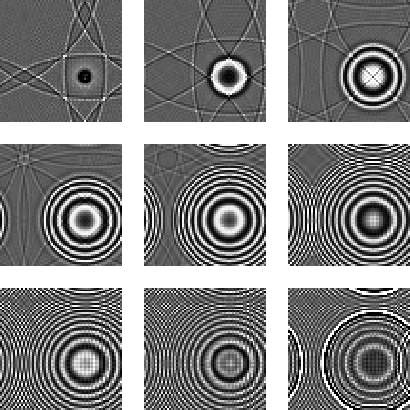
Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) displays time slices through the 3-D cube
of diffraction data obtained using Split-Step modeling.
pspi3Dtimes
displays time slices through the 3-D cube
of diffraction data obtained using Split-Step modeling.
pspi3Dtimes
Figure 7 Time slices through the 3-D diffraction cube (64x64x256) output
of the PSPI modeling program. The wraparound is due
to non-absorbing boundaries.
 split3Dtimes
split3Dtimes
Figure 8 Time slices through the 3-D diffraction cube (64x64x256) output
of the Split-Step modeling program. The wraparound is due
to non-absorbing boundaries.






Next: CONCLUSIONS
Up: THE SPLIT-STEP FOURIER MODELING
Previous: A 2-D example
Stanford Exploration Project
11/18/1997
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) displays time slices through the 3-D cube
of diffraction data obtained using PSPI modeling while
Figure
displays time slices through the 3-D cube
of diffraction data obtained using PSPI modeling while
Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) displays time slices through the 3-D cube
of diffraction data obtained using Split-Step modeling.
displays time slices through the 3-D cube
of diffraction data obtained using Split-Step modeling.