




Next: THE METHOD
Up: Balog: Interpolation
Previous: Balog: Interpolation
Most standard interpolation techniques try to recover the true dips by performing a local search on the data (Bardan, 1987).
Those techniques are very sensitive to the noise level and perform poorly when crossing events are present.
Claerbout proposed a different approach by interpolating with spatial predictors in the (t,x) domain (Claerbout, 1991).
In the same time Spitz presented a method to interpolate seismic traces beyond aliasing in the 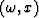 domain (Spitz, 1991).
domain (Spitz, 1991).
The Stanford Exploration Project (SEP) devotes a great deal of effort toward understanding interpolation of aliased seismic data (Nichols, 1990, Ji, 1991).
This paper deals with the implementation of Spitz's method (Spitz, 1991) and the evaluation of the results obtained by testing the program on synthetic and real data.
In the first part I review the theory, in the second I describe the code and in the last I discuss several results and provide an example where the program fails.





Next: THE METHOD
Up: Balog: Interpolation
Previous: Balog: Interpolation
Stanford Exploration Project
12/18/1997