




Next: The Galerkin operator
Up: THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
Previous: THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
The model problem I coded on the CM was a heat flow problem.
The first boundary condition is known as the essential boundary
condition and has to be explicitly applied in the algorithm. The
second boundary conditions is know as the natural boundary condition
and it is the boundary condition implicit in the FE method. This
problem was assigned as part of a computer science course ``Finite
Element Methods for Elliptic PDEs Using Parallel Computers.'' The
problem was solved for a rectangular domain 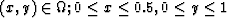 discretized into
discretized into 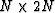 square shaped elements. The domain and the boundary segments are
shown in figure
square shaped elements. The domain and the boundary segments are
shown in figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
domain
.
domain
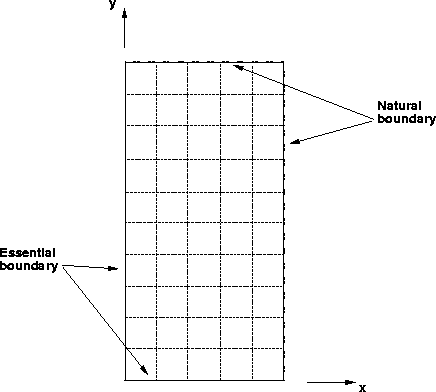
Figure 1 The model domain. Essential boundary conditions are applied on the left and bottom edges; natural boundary conditions apply on the top and right edges.

A suitable form for the elements of the Galerkin operator is
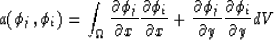





Next: The Galerkin operator
Up: THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
Previous: THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
Stanford Exploration Project
12/18/1997
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
.
![]()