




Next: Flow balancing
Up: EIKONAL EQUATION
Previous: EIKONAL EQUATION
We observe that the gradient components of the eikonal equation satisfy
a hyperbolic conservation law.
First, use 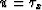 to rewrite equation (1) as
to rewrite equation (1) as
| 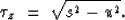 |
(2) |
Second, take the derivative of this equation with respect to x:
| 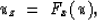 |
(3) |
where the function 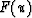 is defined as
is defined as
| 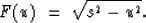 |
(4) |
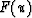 is called the conserved flux; if
is called the conserved flux; if 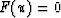 , the rays do not
``flow'' downward anymore, but travel horizontally.
Thus by choosing a positive sign in front of the square root in
equation (2),
and by using
, the rays do not
``flow'' downward anymore, but travel horizontally.
Thus by choosing a positive sign in front of the square root in
equation (2),
and by using 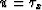 instead of
instead of 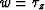 as the substitution
variable, we limit ourselves to time-fields with
downward-traveling rays.
as the substitution
variable, we limit ourselves to time-fields with
downward-traveling rays.
By following analogous reasoning for the z-derivative w
of the time field, and by making the appropriate choices of square
roots, we can build equations for rays traveling in other
directions. These other equations will have to be solved, for
instance, when the field of a point source is being computed, because
the rays then move in all directions.
An alternative approach, which we will follow here, is to write
the eikonal equation in polar coordinates 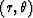 ,
,
| 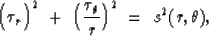 |
(5) |
and solve it along expanding circular fronts. The conserved-flux
function in polar coordinates becomes
| 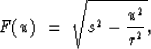 |
(6) |
with 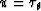 satisfying
satisfying
| 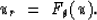 |
(7) |
The above equation (and equation (3)) now has the form of a
hyperbolic conservation law, or flux-conserving equation.
The meaning of this equation is illustrated with an example in the next
section.





Next: Flow balancing
Up: EIKONAL EQUATION
Previous: EIKONAL EQUATION
Stanford Exploration Project
1/13/1998
![]() ,
,