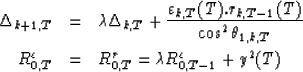Next: Statistical signification of
Up: THE LSL ALGORITHM
Previous: Recursions: time updating
The weighting consists of using a tapering coefficient 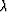 to minimize the weighted norm of the residuals:
to minimize the weighted norm of the residuals:
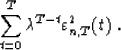
It forces the algorithm to forget the ``old data'' in the minimization
problem: it extends the adaptive properties of the algorithm.
We can use the recursion results derived up to now, simply adapted to
another choice of scalar product:
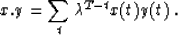
Actually, only the covariances and correlation recursions are modified:
| 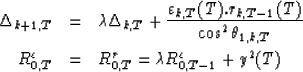 |
(5) |
| |





Next: Statistical signification of
Up: THE LSL ALGORITHM
Previous: Recursions: time updating
Stanford Exploration Project
1/13/1998
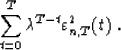
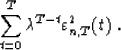
![]()