




Next: Flux-conservative equation
Up: Van Trier: Finite-difference calculation
Previous: Introduction
The Eikonal equation in two dimensions is as follows:
| 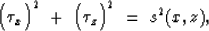 |
(1) |
where s(x,z) is the 2-dimensional slowness model and 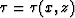 is
the traveltime field. Subscripts x and z denote partial derivatives
with respect to x and z, respectively.
is
the traveltime field. Subscripts x and z denote partial derivatives
with respect to x and z, respectively.
Stanford Exploration Project
1/13/1998