|
|
|
|
Ambient seismic noise eikonal tomography for near-surface imaging at Valhall |
| (12) |
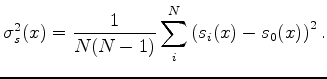 datapoints using
datapoints using 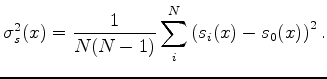 forcing functions weighted by
forcing functions weighted by | (13) |
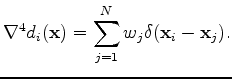 |
(14) |
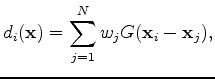 |
(15) |
| (16) |
|
|
|
|
Ambient seismic noise eikonal tomography for near-surface imaging at Valhall |