|
|
|
|
A new bidirectional deconvolution method that overcomes the minimum phase assumption |
|
|---|
|
minwavlet,mod-minwavlet,jonwavlet,mod-jonwavlet,symwavlet,mod-symwavlet
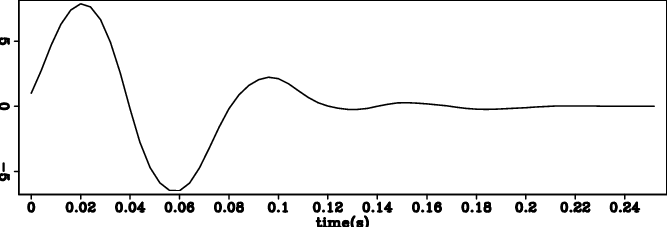
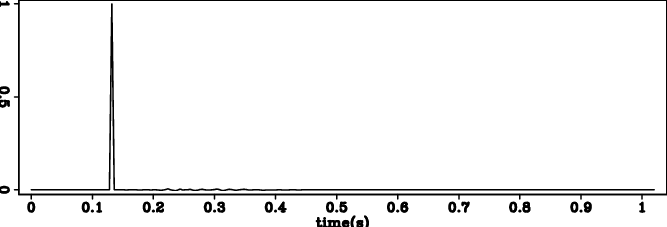
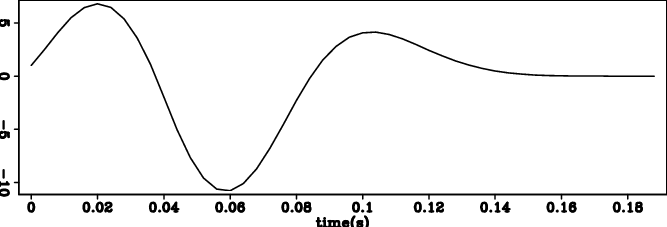
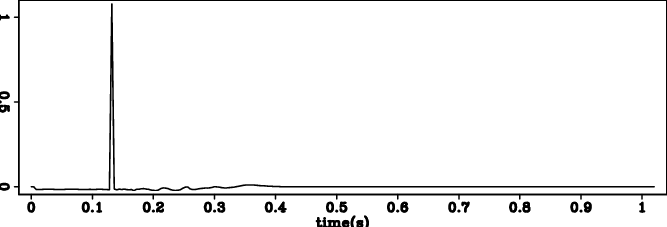
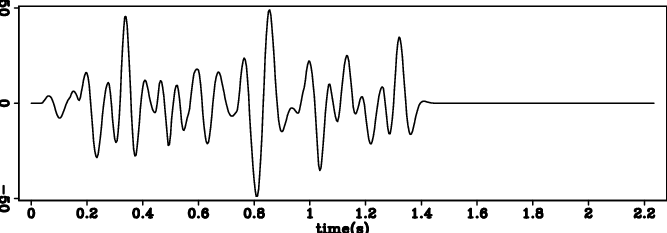
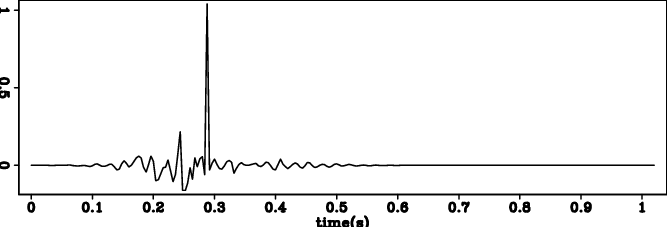
Figure 1. (a) Input wavelet 1 and (b) its deconvolution result. (c) Input wavelet 2 and (b) its deconvolution result. (e) Input wavelet 3 and (f) its deconvolution result. |
|
|
|
|---|
|
fita-symwavlet,fitb-symwavlet
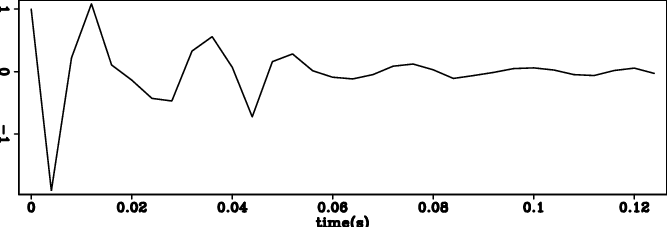
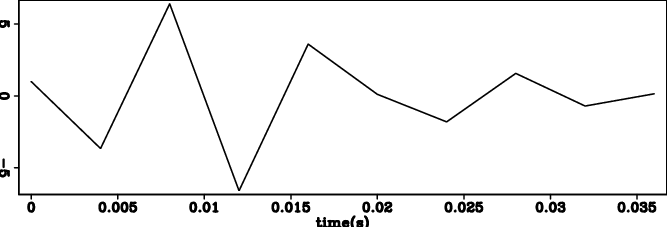
Figure 2. For the wavelet 3 inversion, (a) filter |
|
|
Figure 1(a) 1(b), figure 1(c) 1(d) and figure 1(e) 1(f) show wavelets 1,2,3, and the results of reflectivity models respectively. In all 3 cases, our bidirectional deconvolution method is able to compress the wavelet into a spike.
Figure 2 shows the retrieved
filters ![]() and
and ![]() from wavelet 3's inversion. Notice that
from wavelet 3's inversion. Notice that
![]() and
and ![]() given by the inversion are different from each
other, while ideally they should be the same, since
given by the inversion are different from each
other, while ideally they should be the same, since ![]() and
and ![]() are
the same when we create wavelet 3. This observation indicates that
the solutions
are
the same when we create wavelet 3. This observation indicates that
the solutions ![]() and
and ![]() of this method do not necessarily
converge to the inverse of the initial
of this method do not necessarily
converge to the inverse of the initial ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
|
|
|
|
A new bidirectional deconvolution method that overcomes the minimum phase assumption |