|
|
|
|
Generalized-norm conjugate direction solver |
| Norm | Description | |
| L2 | Conventional |
|
| L1 | ||
| Huber | Huber |
|
| Hybrid |
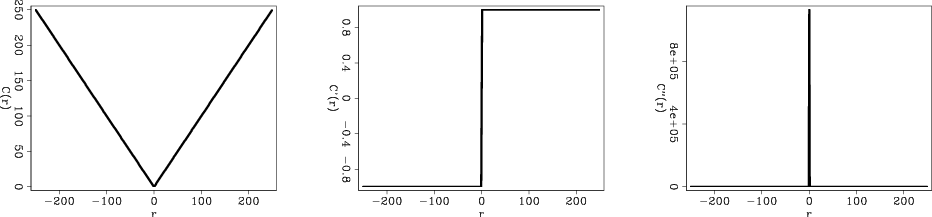
L2 (Least Squares):
| (1) | |||
| (2) | |||
| (3) |
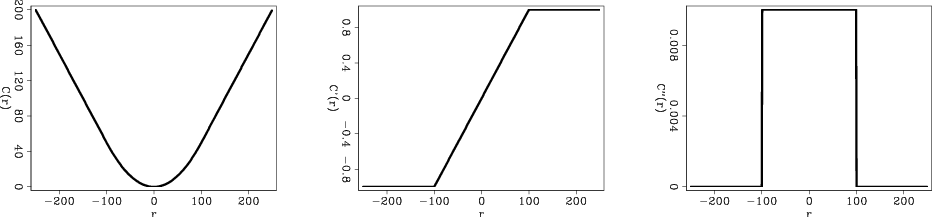
L1:
| (4) | |||
| (5) | |||
| 0 or |
(6) |
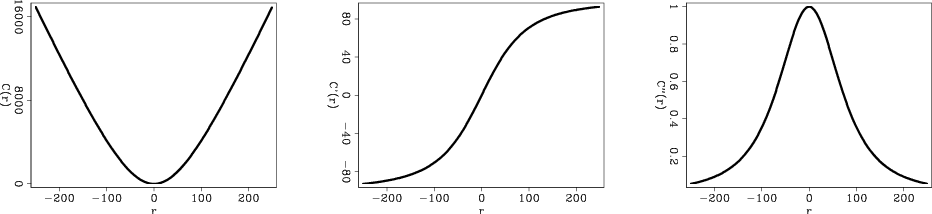
Huber:
| (7) | |||
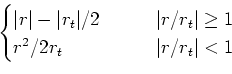 |
(8) | ||
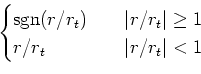 |
(9) |
Hybrid:
 |
(10) | ||
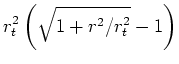 |
(11) | ||
 |
(12) |
|
|---|
|
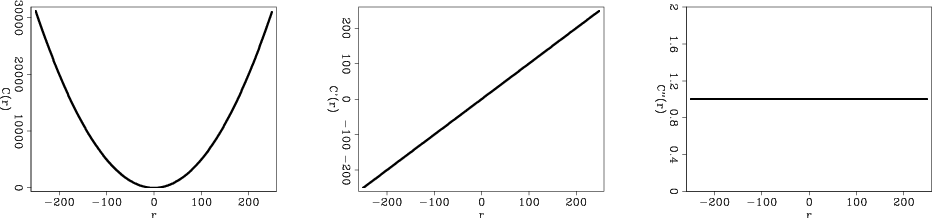
l2-norm,l1-norm,huber-norm,hybrid-norm
Figure 1. Norm functions and their first and second derivatives plotted for |
|
|
The choice of norm is specified as an input argument to our solver. A further benefit of this implementation is that other norms can be added with minimal modification to the overall solver framework. To add a new norm, all that is necessary is adding the appropriate definition of the norm and its derivatives in the code.
|
|
|
|
Generalized-norm conjugate direction solver |