 |
 |
 |
 | Theory and practice of interpolation in the pyramid domain |  |
![[pdf]](icons/pdf.png) |
Next: Transformation artifacts
Up: Theory: introducing the pyramid
Previous: The pyramid transform
The equation of a plane-wave in 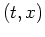 is given by
is given by
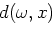 |
(7) |
where  is a waveform and
is a waveform and 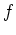 is a constant slope. The
prediction operator
is a constant slope. The
prediction operator 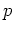 from one trace to another at a distance
from one trace to another at a distance 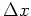 in
in
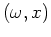 for the plane-wave in equation (7) is given by Fomel (2002):
for the plane-wave in equation (7) is given by Fomel (2002):
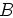 |
(8) |
If we now introduce the new variable
 in equation
(8), then we have a new prediction operator
in equation
(8), then we have a new prediction operator 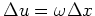 in the
in the
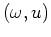 domain:
domain:
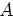 |
(9) |
From Equation (9), we notice that the dependency in
 of the prediction operator has vanished in the pyramid
domain. Sun and Ronen (1996) extend this property to more than one
plane-wave. We illustrate the pyramid domain in Figure 1.
Figure 1a shows two plane-waves with
the same wavelet (Ricker 2 with a fundamental frequency of
20Hz). Figure 1b displays the real
part of the Fourier transformed data in the
of the prediction operator has vanished in the pyramid
domain. Sun and Ronen (1996) extend this property to more than one
plane-wave. We illustrate the pyramid domain in Figure 1.
Figure 1a shows two plane-waves with
the same wavelet (Ricker 2 with a fundamental frequency of
20Hz). Figure 1b displays the real
part of the Fourier transformed data in the 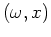 domain and
Figure 1c the real part of the
domain and
Figure 1c the real part of the
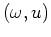 pyramid domain. Notice that we limited the range of
frequencies for display purposes only in Figures
1b and
1c. In 2-D, the pyramid domain maps
into a triangle-shaped area. In 3-D, it will map into a pyramid-shaped
volume. Consequently, each trace in
pyramid domain. Notice that we limited the range of
frequencies for display purposes only in Figures
1b and
1c. In 2-D, the pyramid domain maps
into a triangle-shaped area. In 3-D, it will map into a pyramid-shaped
volume. Consequently, each trace in 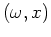 is transformed into a
radial trace in
is transformed into a
radial trace in 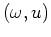 .
.
As anticipated from the definition of the prediction operator
in equation (9), the information at each frequency in
Figure 1c is independent of
 , which means that any scheme involving pefs in
the pyramid domain will require only one filter (one 1-D filter for
2-D data, and one 2-D filter for 3-D data). In addition, we observe
that the slope
, which means that any scheme involving pefs in
the pyramid domain will require only one filter (one 1-D filter for
2-D data, and one 2-D filter for 3-D data). In addition, we observe
that the slope 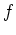 now acts as a wavenumber on the
now acts as a wavenumber on the 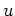 axis.
This fact implies that the low velocity event in
Figure 1a will look like a high
wavenumber component on the
axis.
This fact implies that the low velocity event in
Figure 1a will look like a high
wavenumber component on the 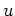 -axis whereas the high velocity event
will look like a low wavenumber.
An added feature is that since we only
have one pef for the whole domain (in theory), the filter estimation
should be relatively robust to the noise present in the data
(especially for random noise).
-axis whereas the high velocity event
will look like a low wavenumber.
An added feature is that since we only
have one pef for the whole domain (in theory), the filter estimation
should be relatively robust to the noise present in the data
(especially for random noise).
 |
 |
 |
 | Theory and practice of interpolation in the pyramid domain |  |
![[pdf]](icons/pdf.png) |
Next: Transformation artifacts
Up: Theory: introducing the pyramid
Previous: The pyramid transform
2009-10-19
![]() , which means that any scheme involving pefs in
the pyramid domain will require only one filter (one 1-D filter for
2-D data, and one 2-D filter for 3-D data). In addition, we observe
that the slope
, which means that any scheme involving pefs in
the pyramid domain will require only one filter (one 1-D filter for
2-D data, and one 2-D filter for 3-D data). In addition, we observe
that the slope ![]() now acts as a wavenumber on the
now acts as a wavenumber on the ![]() axis.
This fact implies that the low velocity event in
Figure 1a will look like a high
wavenumber component on the
axis.
This fact implies that the low velocity event in
Figure 1a will look like a high
wavenumber component on the ![]() -axis whereas the high velocity event
will look like a low wavenumber.
An added feature is that since we only
have one pef for the whole domain (in theory), the filter estimation
should be relatively robust to the noise present in the data
(especially for random noise).
-axis whereas the high velocity event
will look like a low wavenumber.
An added feature is that since we only
have one pef for the whole domain (in theory), the filter estimation
should be relatively robust to the noise present in the data
(especially for random noise).