 |
 |
 |
 | Kinematics in iterated correlations of a passive acoustic experiment |  |
![[pdf]](icons/pdf.png) |
Next: Green's function in the
Up: Wave equation and Green's
Previous: Fourier Transformations
Using the forward Fourier transformation equation A-2, the wave equation for pressure in a homogeneous medium with
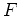 is written in the frequency-domain as
is written in the frequency-domain as
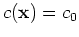 |
(65) |
The frequency-domain Green's function
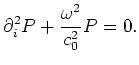 is defined by introducing an impulsive point source acting at
is defined by introducing an impulsive point source acting at 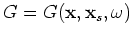 and
and
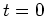 on the right-hand side of equation A-4 as follows:
on the right-hand side of equation A-4 as follows:
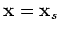 |
(66) |
The Green's function solution for two-dimensional space, under the far field approximation can be obtained as
![$\displaystyle G(\mathbf{x},\mathbf{x}_s,\omega) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{8\pi\omega c_0...
...\left\vert \mathbf{x}-\mathbf{x}_s \right\vert + \frac{\pi}{4} \right] \right).$](img192.png) |
(67) |
A source function is easily included by multiplication with the frequency-domain source function. A measurement,
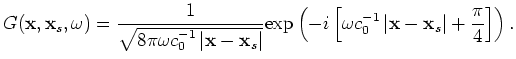 , at a station located at
, at a station located at
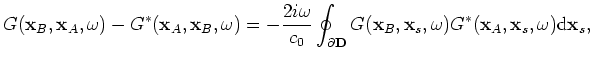 of a source at
of a source at
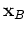 emitting a source function
emitting a source function 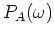 is obtained as follows:
is obtained as follows:
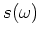 |
(68) |
The sources in this paper are simulated emitting zero-phase Ricker wavelets with center frequency 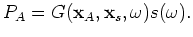 . The frequency-domain expression used is
. The frequency-domain expression used is
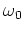 |
(69) |
 |
 |
 |
 | Kinematics in iterated correlations of a passive acoustic experiment |  |
![[pdf]](icons/pdf.png) |
Next: Green's function in the
Up: Wave equation and Green's
Previous: Fourier Transformations
2009-05-05
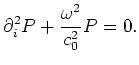 is defined by introducing an impulsive point source acting at
is defined by introducing an impulsive point source acting at ![]() and
and
![]() on the right-hand side of equation A-4 as follows:
on the right-hand side of equation A-4 as follows:
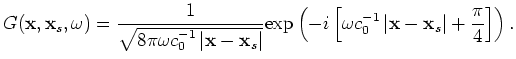 , at a station located at
, at a station located at
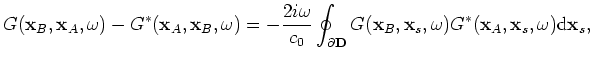 of a source at
of a source at
![]() emitting a source function
emitting a source function ![]() is obtained as follows:
is obtained as follows: