|
|
|
|
Seismic imaging using GPGPU accelerated reverse time migration |
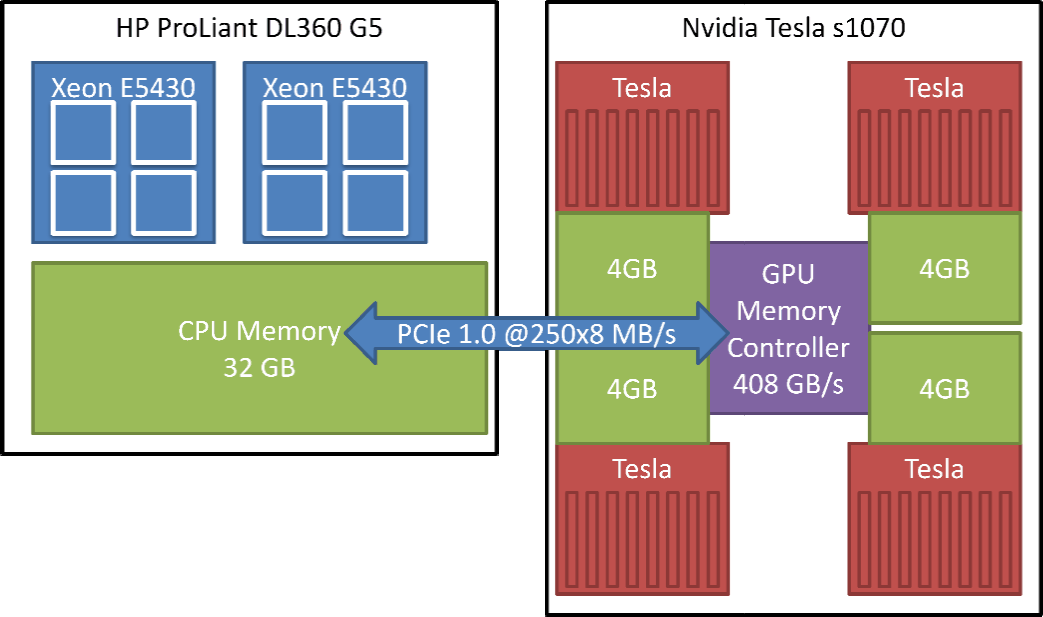
The basic architecture consists of a ``Host System,'' using regular CPUs and running a standard Linux operating system. Attached is the ``Device,'' a 1U rack-mounted GPGPU accelerator which provides the parallelism discussed in earlier sections. The CUDA technology uses the terms ``host'' and ``device'' to refer to the various hardware and software abstractions that apply to either CPU or GPU systems. Although the S1070 has four GPUs, it is considered one ``device''; and similarly, there is one ``host,'' although it has 8 CPU cores in this system. Below is a summary of the system specifications:
Host: HP ProLiant DL360 G5 (HP ProLiant series, 2009) (HP ProLiant DL360G5 Overview, 2009)
Device: Nvidia Tesla S1070 Computing System (S1070 Product Information, 2009)
|
|---|
|
hostDeviceInterconnectSchem
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the Host-Device (CPU-GPU) interconnection and memory structure. The compartmental memory structure on the Device side is problematic for multi-GPU programs, because it severely restricts shared memory methods. Much of my recent implementation efforts address this issue. [NR] |
|
|
The S1070 is a very recently released commercial platform specifically tailored for high-performance scientific computing. Nvidia recommends using it only with certain host hardware environments. The system installation procedure is explained in the appendix, along with solutions to difficulties that may be encountered.
The final system environment runs CENTOS 5.2 for x86_64 and using the Nvidia Tesla Driver (Linux x86_64 - 177.70.11). Two Host Interconnect Cards (HIC) are installed and configured in the ProLiant. Both cards are connected to the S1070 unit via two PCI-e cables. This setup produces a reliable and functional system for GPGPU computational acceleration.
|
|---|
|
teslaRackMountPhoto
Figure 2. Rack mount view of the SEP Tesla system. At the top is the S1070 1U 4xGPU GPGPU Computing Appliance. Below is the HP ProLiant Xeon 64 bit, 8 core (2xSMP, 4xCMP) system, tesla0.stanford.edu which runs the host operating system. [NR] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Seismic imaging using GPGPU accelerated reverse time migration |