|
|
|
|
Measuring image focusing for velocity analysis |
The interpolation defined by 5
depends in a non-straightforward manner
from both angles ![]() and
and ![]() ,
as well as from the estimate
of the local dip
,
as well as from the estimate
of the local dip
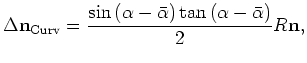 .
Although,
this is the relationship I used in practice for the examples in this
paper, I will now analyze one of its variants that is simpler
and thus it helps
to better understand the relationship between
image curvature and residual migration parameter.
.
Although,
this is the relationship I used in practice for the examples in this
paper, I will now analyze one of its variants that is simpler
and thus it helps
to better understand the relationship between
image curvature and residual migration parameter.
I start from redefining residual migration in the
pseudo-depth domain
![]() (Sava, 2004).
In this domain,
the focusing/unfocusing effects of residual migration
are better separated from its mapping effects than in the conventional
depth domain.
In the pseudo-depth domain,
normal-incidence images of flat reflectors
are not shifted by residual migration.
The expression of residual migration 4 becomes:
(Sava, 2004).
In this domain,
the focusing/unfocusing effects of residual migration
are better separated from its mapping effects than in the conventional
depth domain.
In the pseudo-depth domain,
normal-incidence images of flat reflectors
are not shifted by residual migration.
The expression of residual migration 4 becomes:
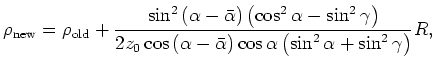 ) of normal incidence images (
) of normal incidence images (
However, in the special case of events that are locally flat (
![]() )
and are imaged at normal-incidence (i.e.
)
and are imaged at normal-incidence (i.e. ![]() ),
this expression simplifies into:
),
this expression simplifies into:
|
|
|
|
Measuring image focusing for velocity analysis |