




Next: About this document ...
Up: REFERENCES
Previous: REFERENCES
Waveform extrapolation employing forward modeling in Riemannian
coordinates Sava and Fomel (2005); Shragge (2006) does not present a
problem for general approach to waveform inversion developed herein
because inversion does not take
place in generalized coordinates. Rather, the calculated Green's
functions are transformed back to global Cartesian grid through
mapping pair
| 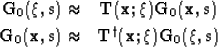 |
(38) |
| (39) |
where 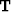 is a transformation matrix that interpolates from the
Riemannian space defined by
is a transformation matrix that interpolates from the
Riemannian space defined by 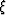 to global Cartesian space
to global Cartesian space  that
includes the transformation Jacobian. In practice, this is applied
using weighted sinc interpolation. Thus, one may rewrite the adjoint
of equation 27 in the following manner
that
includes the transformation Jacobian. In practice, this is applied
using weighted sinc interpolation. Thus, one may rewrite the adjoint
of equation 27 in the following manner
| 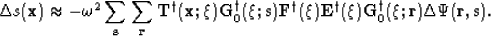 |
(40) |





Next: About this document ...
Up: REFERENCES
Previous: REFERENCES
Stanford Exploration Project
5/6/2007